Escape for the Weekend
Explore our collection of weekend
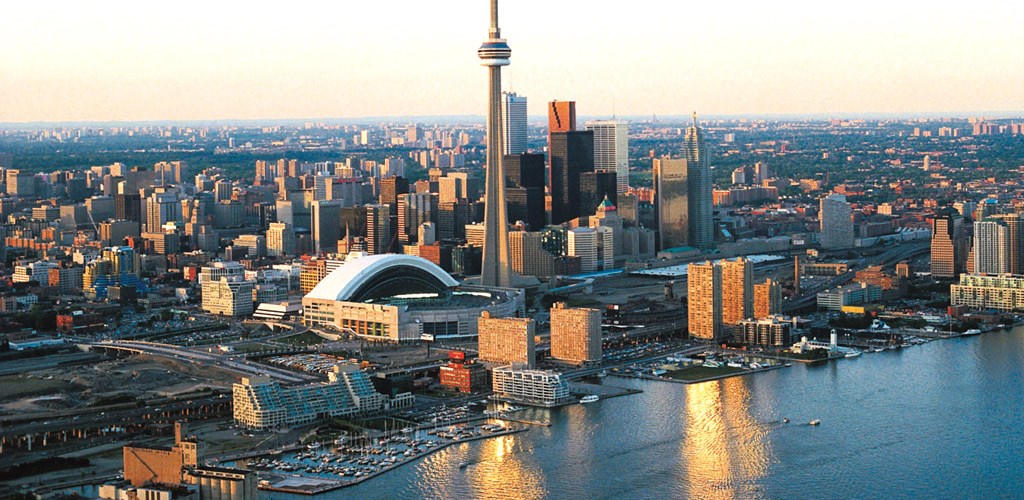
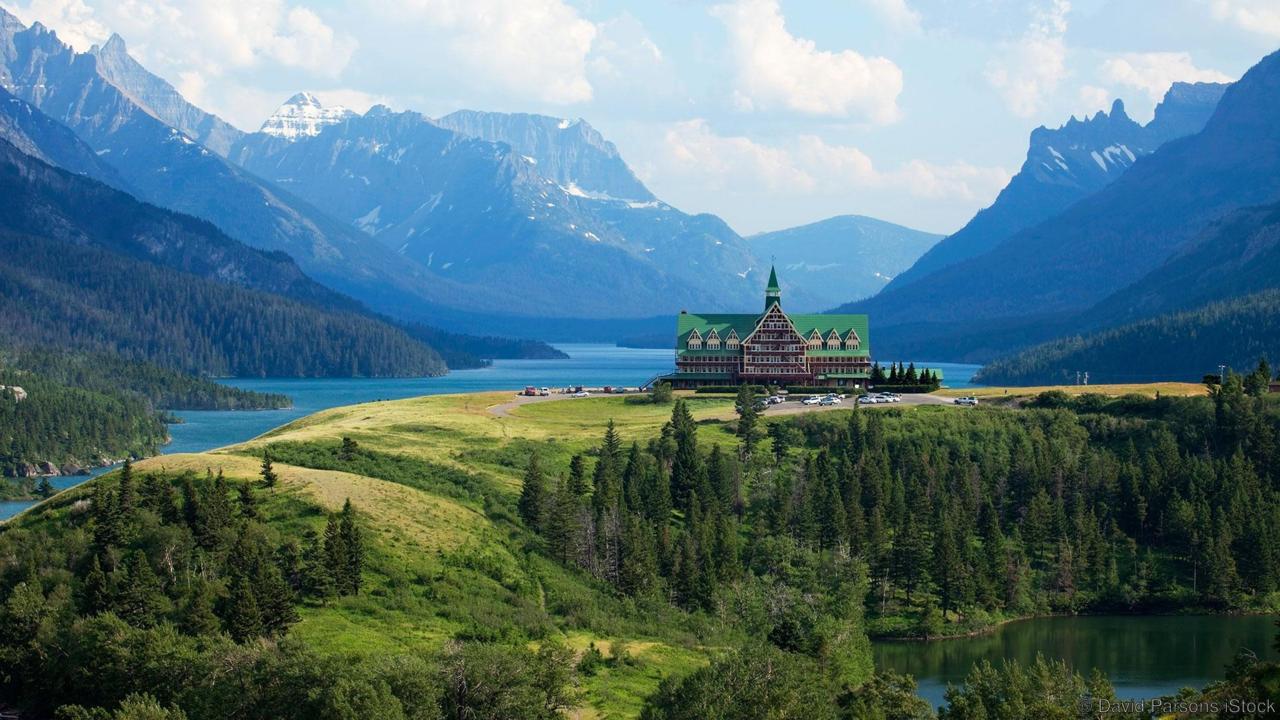
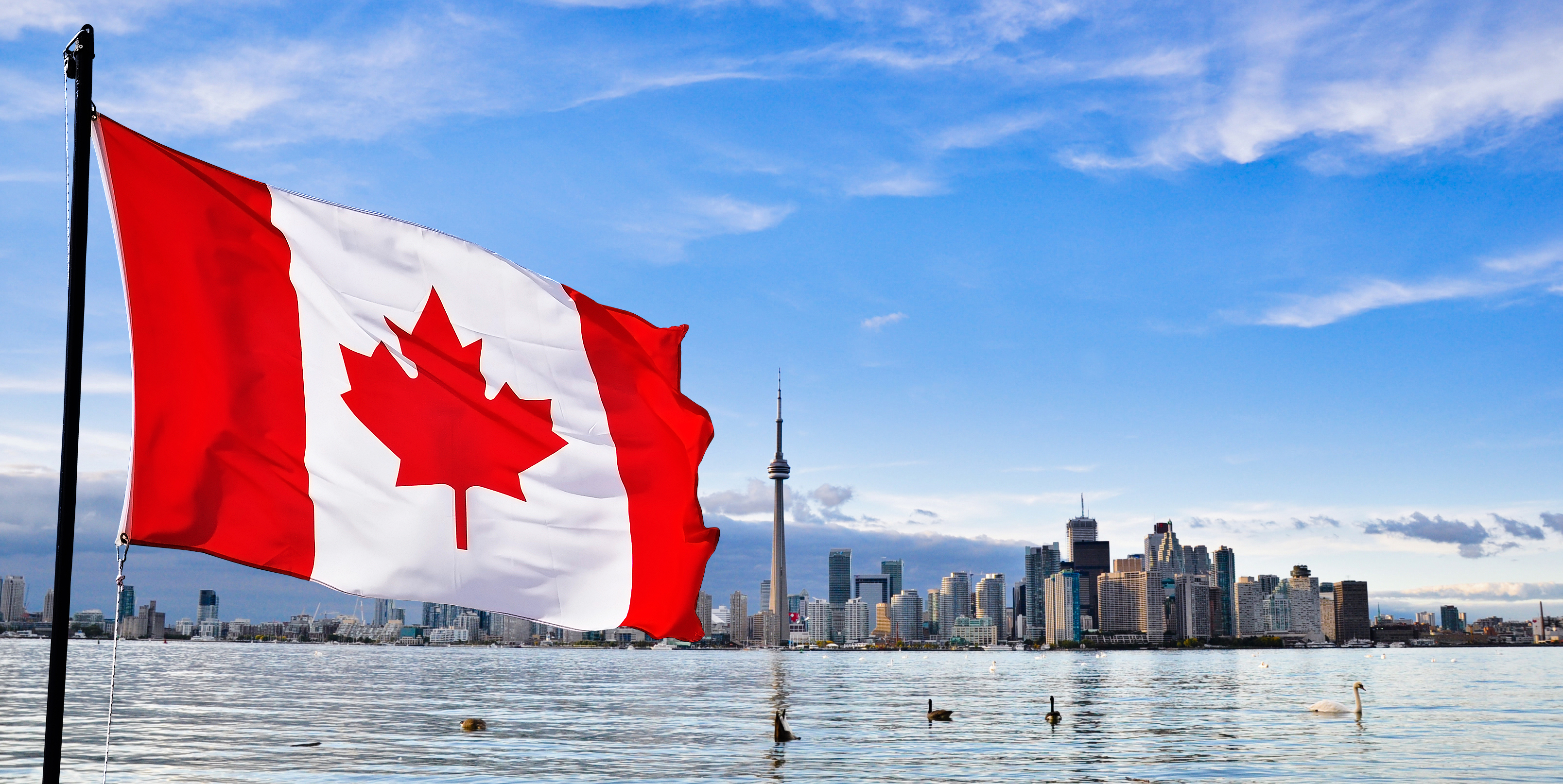
Canada
Canada is a country in the northern part of North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic to the Pacific and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering 9.98 million square kilometres (3.85 million square miles), making it the world's second-largest country by total area and the fourth-largest country by land area. Canada's sole border with the United States is the world's longest bi-national land border. The majority of the country has a cold or severely cold winter climate, but southerly areas are warm in summer. Canada is sparsely populated, the majority of its land territory being dominated by forest and tundra and the Rocky Mountains. It is highly urbanized with 82 per cent of the 35.15 million people concentrated in large and medium-sized cities, many near the southern border. Its capital is Ottawa, and its largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal and Vancouver.
Canada is a country in the northern part of North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic to the Pacific and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering 9.98 million square kilometres (3.85 million square miles), making it the world's second-largest country by total area and the fourth-largest country by land area. Canada's sole border with the United States is the world's longest bi-national land border. The majority of the country has a cold or severely cold winter climate, but southerly areas are warm in summer. Canada is sparsely populated, the majority of its land territory being dominated by forest and tundra and the Rocky Mountains. It is highly urbanized with 82 per cent of the 35.15 million people concentrated in large and medium-sized cities, many near the southern border. Its capital is Ottawa, and its largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal and Vancouver.
Various indigenous peoples had inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years prior to European colonization. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French claims were made on the area, with the colony of Canada first being established by the French in 1535 during Jacques Cartier's second voyage to New France. As a consequence of various conflicts, Great Britain gained and lost territories within British North America until it was left, in the late 18th century, with what mostly geographically comprises Canada today. Pursuant to the British North America Act, on July 1, 1867, the colonies of Canada, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia joined to form the semi-autonomous federal Dominion of Canada. This began an accretion of provinces and territories to the mostly self-governing Dominion to the present ten provinces and three territories forming modern Canada.
In 1931, Canada achieved near-total independence from the United Kingdom with the Statute of Westminster 1931, but at the time, Canada decided to allow the British Parliament to temporarily retain the power to amend Canada's constitution, on request from the Parliament of Canada. With the Constitution Act 1982, Canada took over that authority (as the conclusion of Patriation), removing the last remaining ties of legal dependence on the British Parliament, giving the country full sovereignty.
Canada is a federal parliamentary democracy and a constitutional monarchy, with Queen Elizabeth II being the head of state. The country is officially bilingual at the federal level. It is one of the world's most ethnically diverse and multicultural nations, the product of large-scale immigration from many other countries. Its advanced economy is the tenth-largest in the world, relying chiefly upon its abundant natural resources and well-developed international trade networks. Canada's long and complex relationship with the United States has had a significant impact on its economy and culture.
Canada is a developed country and has the tenth-highest nominal per capita income globally as well as the ninth-highest ranking in the Human Development Index. It ranks among the highest in international measurements of government transparency, civil liberties, quality of life, economic freedom, and education. Canada is a realm within the Commonwealth of Nations, a member of the Francophonie, and part of several major international and intergovernmental institutions or groupings including the United Nations, the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, the G7 (formerly G8), the Group of Ten, the G20, the North American Free Trade Agreement and the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation forum.
This is a list of international airports in Canada. These airports are listed in the Canada Flight Supplement, or Water Aerodrome Supplement, published by Nav Canada and each is classified as an airport of entry. All these airports, with the exception of military airports, have a Canada Border Services Agency person available but they may not be available 24 hours a day and may only be open part of the week. Montréal-Pierre Elliott Trudeau International Airport serves a higher percentage of international passengers than any other Canadian airport.[1]
Of the airports below, only 13 are designated as international airports by Transport Canada[citation needed]: St John's, Gander, Halifax, Moncton, Fredericton, Quebec, Montreal, Toronto, Ottawa, Winnipeg, Calgary, Edmonton and Vancouver.
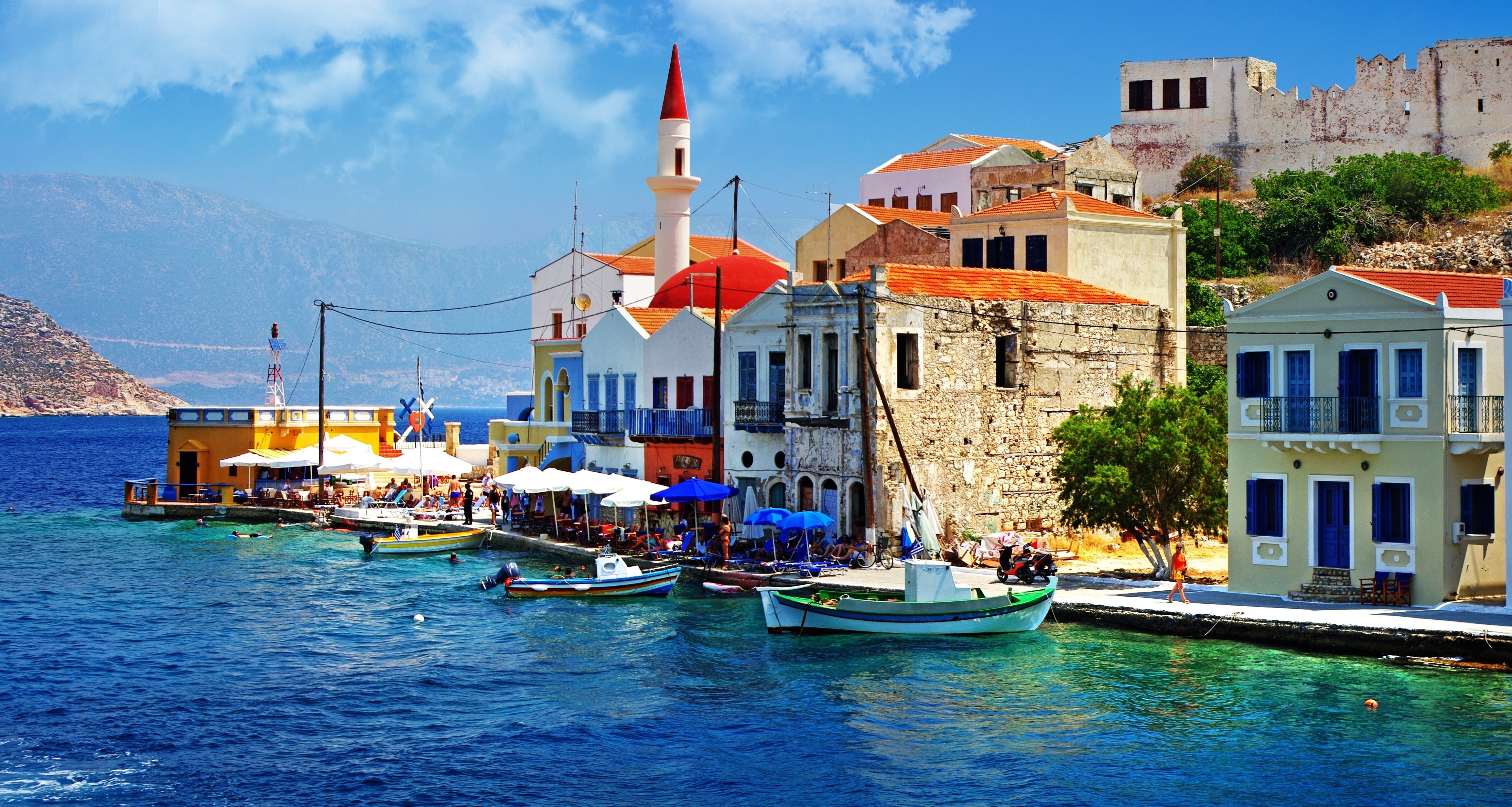
Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (/kəˈnɛəri ˈaɪləndz/; Spanish: Islas Canarias [ˈizlas kaˈnaɾjas], locally: [ˈiʱlːaʰ kaˈnaːɾjaʰ]), also known as the Canaries (Spanish: Canarias), are an archipelago and autonomous community of Spain located on the Atlantic Ocean, 100 kilometres (62 miles) west of Morocco. The Canaries are among the outermost regions (OMR) of the European Union proper. It is also one of the eight regions with special consideration of historical nationality recognized as such by the Spanish Government.[3][4]
The Canary Islands (/kəˈnɛəri ˈaɪləndz/; Spanish: Islas Canarias [ˈizlas kaˈnaɾjas], locally: [ˈiʱlːaʰ kaˈnaːɾjaʰ]), also known as the Canaries (Spanish: Canarias), are an archipelago and autonomous community of Spain located on the Atlantic Ocean, 100 kilometres (62 miles) west of Morocco. The Canaries are among the outermost regions (OMR) of the European Union proper. It is also one of the eight regions with special consideration of historical nationality recognized as such by the Spanish Government.[3][4]
The main islands are (from largest to smallest) Tenerife, Fuerteventura, Gran Canaria, Lanzarote, La Palma, La Gomera and El Hierro. The archipelago also includes a number of islands and islets: La Graciosa, Alegranza, Isla de Lobos, Montaña Clara, Roque del Oeste and Roque del Este. In ancient times, the island chain was often referred to as "the Fortunate Isles".[5] The Canary Islands is the most southerly region of Spain and the largest and most populated archipelago of the Macaronesia region.[6]
The archipelago's beaches, climate and important natural attractions, especially Maspalomas in Gran Canaria and Teide National Park and Mount Teide (a World Heritage Site) in Tenerife (the third tallest volcano in the world measured from its base on the ocean floor), make it a major tourist destination with over 12 million visitors per year, especially Gran Canaria, Tenerife, Fuerteventura and Lanzarote.[7][8] The islands have a subtropical climate, with long hot summers and moderately warm winters.[9] The precipitation levels and the level of maritime moderation varies depending on location and elevation. Green areas as well as desert exist on the archipelago. Due to their location above the temperature inversion layer, the high mountains of these islands are ideal for astronomical observation. For this reason, two professional observatories, Teide Observatory on the island of Tenerife and Roque de los Muchachos Observatory on the island of La Palma, have been built on the islands.
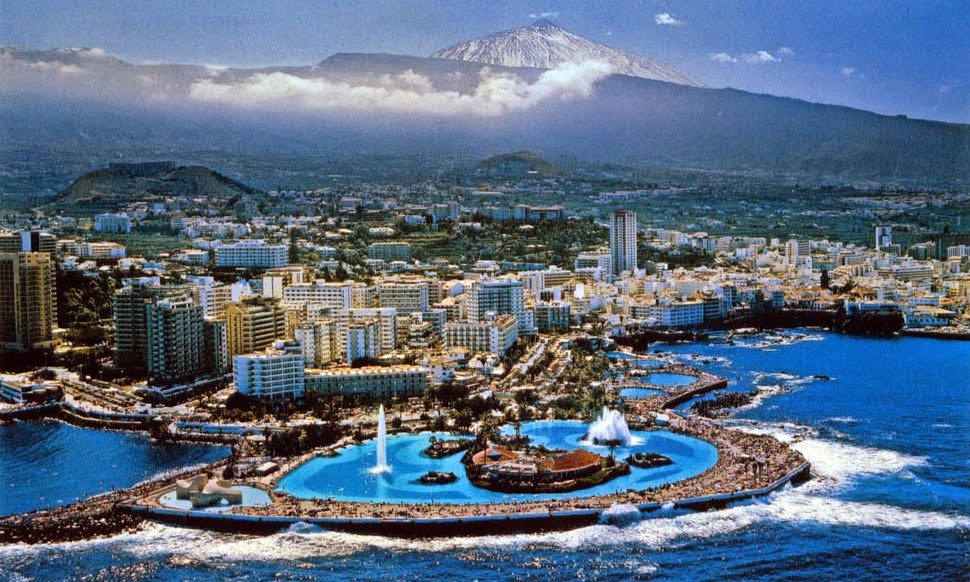
The capital of the Autonomous Community is shared by the cities of Santa Cruz de Tenerife and Las Palmas de Gran Canaria,[10][11] which in turn are the capitals of the provinces of Santa Cruz de Tenerife and Province of Las Palmas. Las Palmas de Gran Canaria has been the largest city in the Canaries since 1768, except for a brief period in the 1910s.[12] Between the 1833 territorial division of Spain and 1927 Santa Cruz de Tenerife was the sole capital of the Canary Islands. In 1927 a decree ordered that the capital of the Canary Islands be shared, as it remains at present.[13][14] The third largest city of the Canary Islands is San Cristóbal de La Laguna (a World Heritage Site) on Tenerife.[15][16][17] This city is also home to the Consejo Consultivo de Canarias, which is the supreme consultative body of the Canary Islands.[18]
During the time of the Spanish Empire, the Canaries were the main stopover for Spanish galleons on their way to the Americas, which came south to catch the prevailing northeasterly trade winds.
The Canary Islands have eight airports altogether, two of the main ports of Spain, and an extensive network of autopistas (highways) and other roads. For a road map see multimap.[73]
There are large ferry boats that link islands as well as fast ferries linking most of the islands. Both types can transport large numbers of passengers and cargo (including vehicles). Fast ferries are made of aluminium and powered by modern and efficient diesel engines, while conventional ferries have a steel hull and are powered by heavy oil. Fast ferries travel relatively quickly (in excess of 30 knots) and are a faster method of transportation than the conventional ferry (some 20 knots). A typical ferry ride between La Palma and Tenerife may take up to eight hours or more while a fast ferry takes about 2 and a half hours and between Tenerife and Gran Canaria can be about one hour.
The largest airport is the Gran Canaria Airport. Tenerife has two airports, Tenerife North Airport and Tenerife South Airport.[74] The island of Tenerife gathers the highest passenger movement of all the Canary Islands through its two airports.[75] The two main islands (Tenerife and Gran Canaria) receive the greatest number of passengers.[76] Tenerife 6,204,499 passengers and Gran Canaria 5,011,176 passengers.[77]
The port of Las Palmas is first in freight traffic in the islands,[78] while the port of Santa Cruz de Tenerife is the first fishing port with approximately 7,500 tons of fish caught, according to the Spanish government publication Statistical Yearbook of State Ports. Similarly, it is the second port in Spain as regards ship traffic, only surpassed by the Port of Algeciras Bay.[79] The port's facilities include a border inspection post (BIP) approved by the European Union, which is responsible for inspecting all types of imports from third countries or exports to countries outside the European Economic Area. The port of Los Cristianos (Tenerife) has the greatest number of passengers recorded in the Canary Islands, followed by the port of Santa Cruz de Tenerife.[80] The Port of Las Palmas is the third port in the islands in passengers and first in number of vehicles transported.[80]
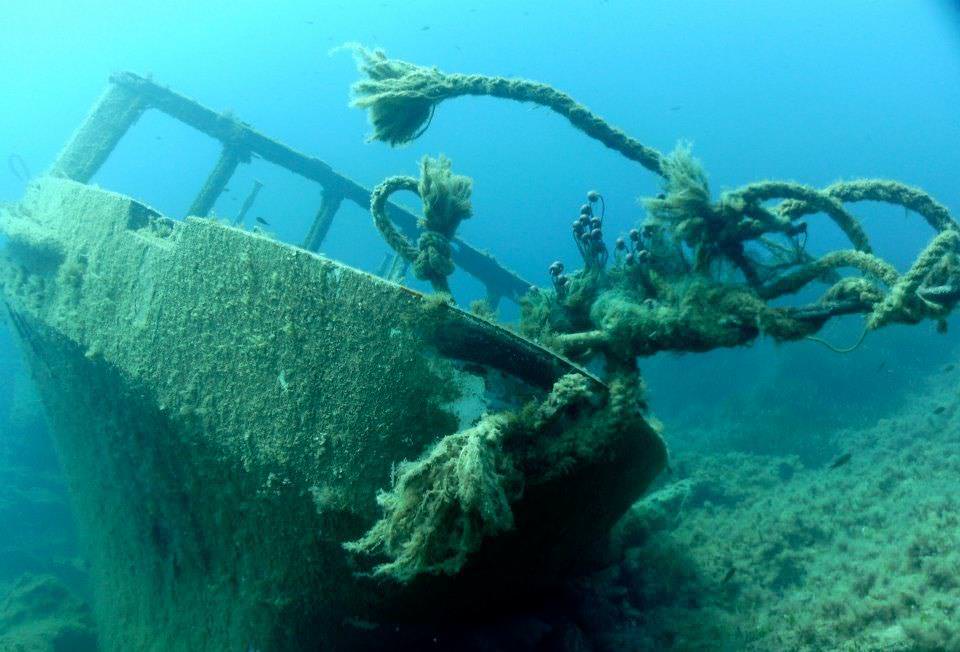
The wreck of American Star (SS America) seen in July 2004 from land side.The SS America was beached at the Canary islands, in the nineties. However, the ocean liner fell apart after some years and parts of ship washed away.
Rail transport[edit]
The Tenerife Tram opened in 2007 and the only one in the Canary Islands, travelling between the cities of Santa Cruz de Tenerife and San Cristóbal de La Laguna. It is currently planned to have three lines in the Canary Islands (two in Tenerife and one in Gran Canaria). The planned Gran Canaria tram route will be from Las Palmas de Gran Canaria to Maspalomas (south).[81]
Airports[edit]
- Tenerife South Airport – Tenerife
- Tenerife North Airport – Tenerife
- Lanzarote Airport – Lanzarote
- Fuerteventura Airport – Fuerteventura
- Gran Canaria Airport – Gran Canaria
- La Palma Airport – La Palma
- La Gomera Airport – La Gomera
- El Hierro Airport – El Hierro[82]
Ports[edit]
- Port of Puerto del Rosario – Fuerteventura
- Port of Arrecife – Lanzarote
- Port of Santa Cruz de La Palma – La Palma
- Port of San Sebastián de La Gomera – La Gomera
- Port of La Estaca – El Hierro
- Port of Las Palmas – Gran Canaria
- Port of Agaete – Gran Canaria
- Port of Los Cristianos – Tenerife
- Port of Santa Cruz de Tenerife – Tenerife
- Port of Garachico – Tenerife
- Port of Granadilla – Tenerife
Canary Islands
The Fortunate (for Divers) Islands
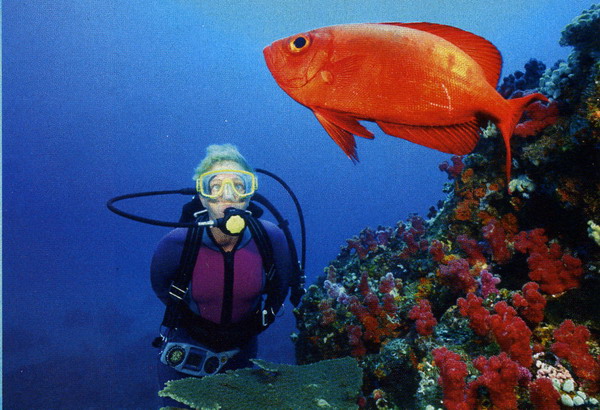
Year-round sun, warm, clear water and dramatic underwater volcanic seascapes draw divers to the Canary Islands. Sometimes called “The Fortunate Islands” due to the subtropical climate and sandy beaches, the islands of this Spanish archipelago lie at the eastern edge of the Atlantic Ocean, off the northwest coast of Africa. The Canaries, as they’re also known, were an important port-of-call for Spanish galleons taking advantage of the trade winds on their way to the Americas.
The seven largest islands – Tenerife, Fuerteventura, Gran Canaria, Lanzarote, La Palma, La Gomera and El Hierro – are premier European tourist destinations and attract more than 12 million visitors a year. Those who come can pick their spot and choose from bustling cities with great nightlife or sleepy little villages where stress just rolls away.
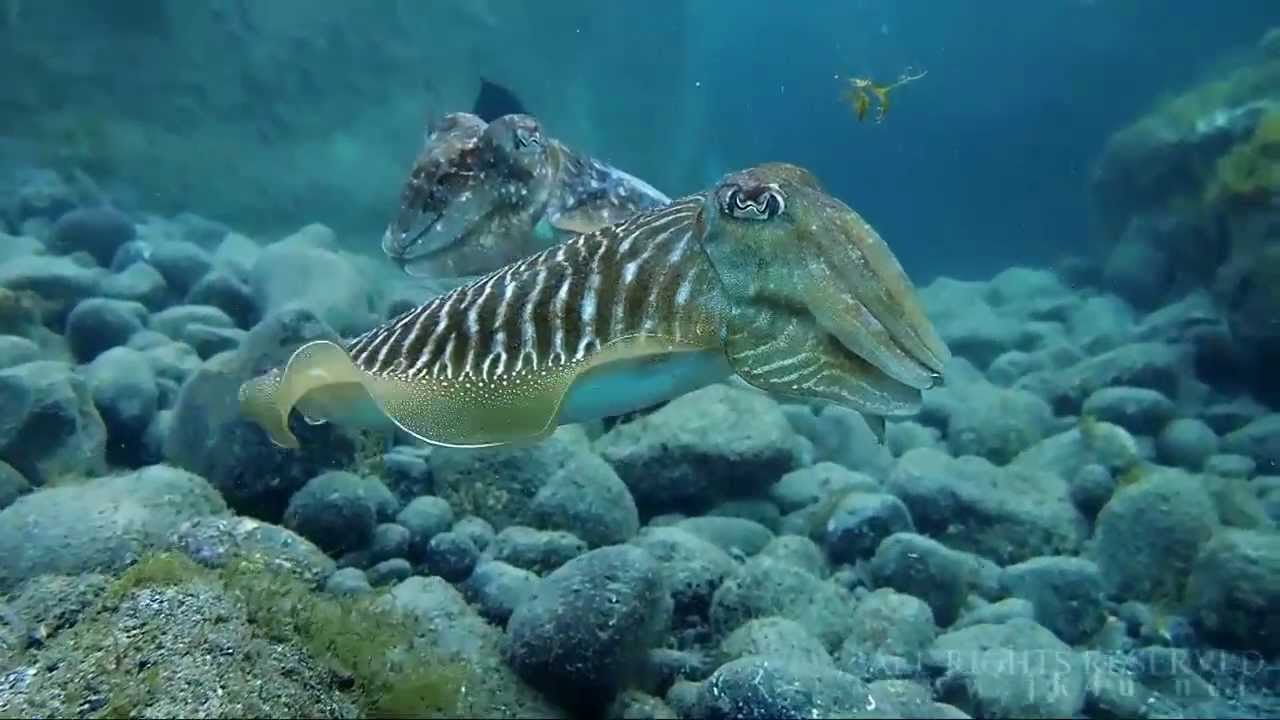
And that’s before you even get to the diving. Visibility of more than 30 metres/100 feet is normal, and water temperatures never drop much below 17-18° C/63-64° F, making it easy to enjoy the unique biodiversity. Divers will encounter both Atlantic and Mediterranean species, and some endemic to the islands themselves.
Great Dives
- La Catedral – This site in Gran Canaria is considered one of the top dives in the region due to the unusual and impressive volcanic formations. Off the coast of La Isleta, just north of Las Palmas, is a morass of lava tubes, caves, arches and crevices. You’ll need a boat and local knowledge to enjoy the best dive on this site.
- The Arona - For shipwreck lovers, Las Palmas in Gran Canaria has a variety of wrecks; some say these are among the best in the world. The Arona is basically in one piece, lying on its side in 40 metres/130 feet of water. It’s well known for the schools of barracuda and other pelagics that patrol her hulk.
- La Restinga - There is a marine reserve on El Hierro where turtles, tuna and dolphins abound; even whale sharks put in an occasional appearance. As recently as 2011, an underwater volcano erupted here, and already marine life is moving back in. El Hierro is the smallest of the Canary Islands and is a bit remote – you have to fly to Tenerife and get a ferry – but the diving makes up for the effort.
- La Burrera - Just off the small island of La Graciosa to the north of Lanzarote lies this site highlighted by a dramatic underwater seascape including pinnacles, columns and large rocky ledges. Marine life is protected here and thrives.
- Cuevo Del Palm Mar – Located ten minutes from Los Cristianos and Las Galletas in Tenerife, is a thrill for advanced and deep divers. Crystal clear water gives incredible visibility to view large rocks, a cave, lobsters, Atlantic barracudas and several species of moray eels. Though gentle and inquisitive, some of these toothy eels are quite ferocious looking.
Want to know more? Visit ScubaEarth® for further information on thousands of dive sites, marine species, destination essentials and more.
Dive Summary
Visibility – Excellent, often exceeds 30 metres/100 feet, depending on local conditions.
Water Temperature – The Canary Islands are bathed by the Gulf Stream, which regulates the water temperature, keeping it between 17-18° C/63-64° F in winter and around 23°C/73°F in summer. Typically, 5mm wet suits in summer and 7mm suits in winter keep divers comfortable.
Weather – Mainly mild winters and warm summers. Year-round warm, sunny weather with average temperatures varying from 17°C in the winter to 24°C in the summer.
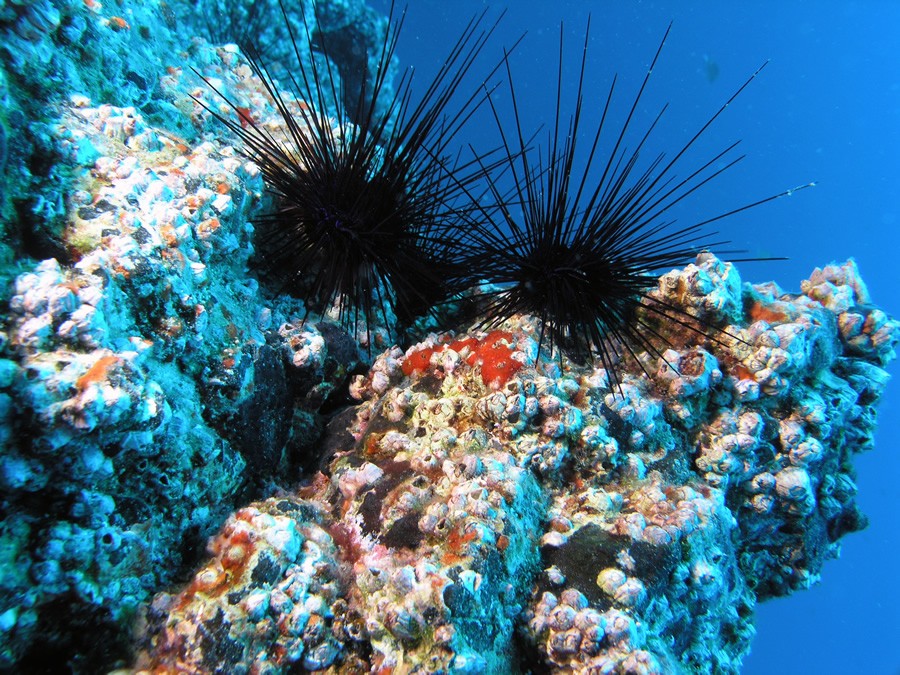
Featured Creatures - Fish species include sharks, rays, bream, jacks, grunts, scorpionfish, triggerfish, groupers, gobies and blennies. Invertebrates include sponges, sea fans, jellyfish, anemones, crabs, sea urchins and more.
Recommended Training – Take the PADI Deep Diver and PADI Wreck Diver courses for diving on the deeper wrecks. The AWARE – Fish Identification specialty course is also a good choice to help you identify the many unique species.
Travel Info
Note - Travel to any destination may be adversely affected by conditions including (but not limited) to security, entry and exit requirements, health conditions, local laws and culture, natural disasters and climate. Regardless of your destination, check your local travel advisory board or department for travel advice about that location when planning your trip and again shortly before you leave.
Language - Spanish, with English, French and German spoken in tourist areas.
Currency - Euro. Credit cards are accepted in hotels and tourist-oriented businesses.
Major Airports - Tenerife, Lanzarote, Gran Canaria and La Palma
Electricity and Internet - 220 volts 50hz; European Type C or type E/F two-pin
Topside Attractions - Take a hike up the side of a volcano in a national park, enjoy the buzz of the big busy tourist towns or relax on a beach enjoying the best climate in the world.
China
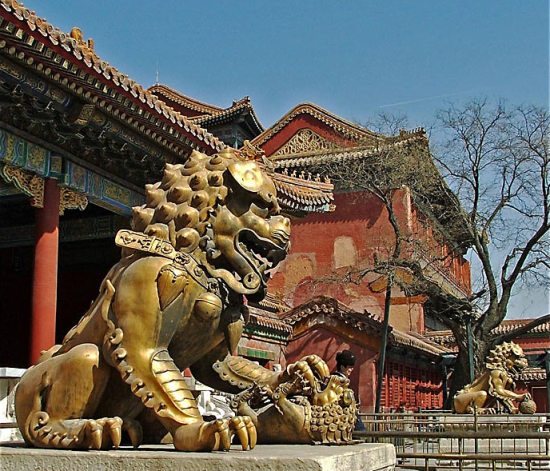
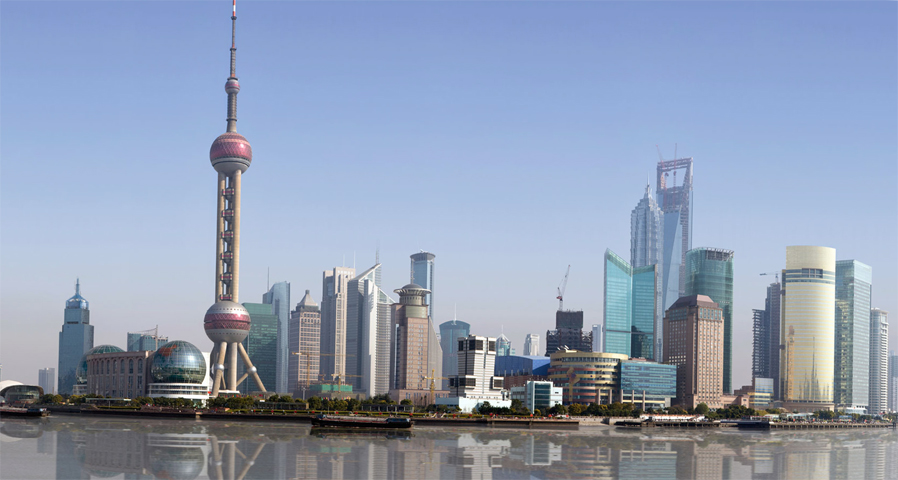
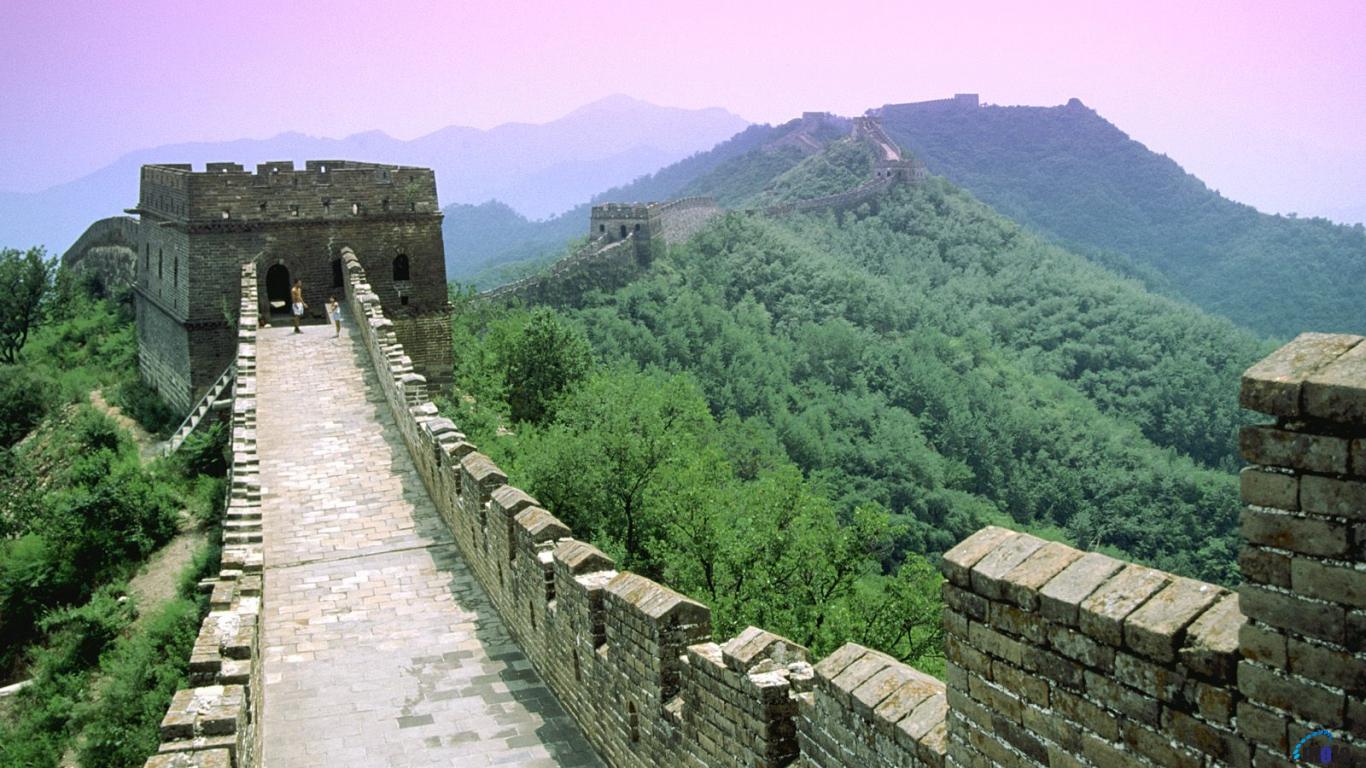
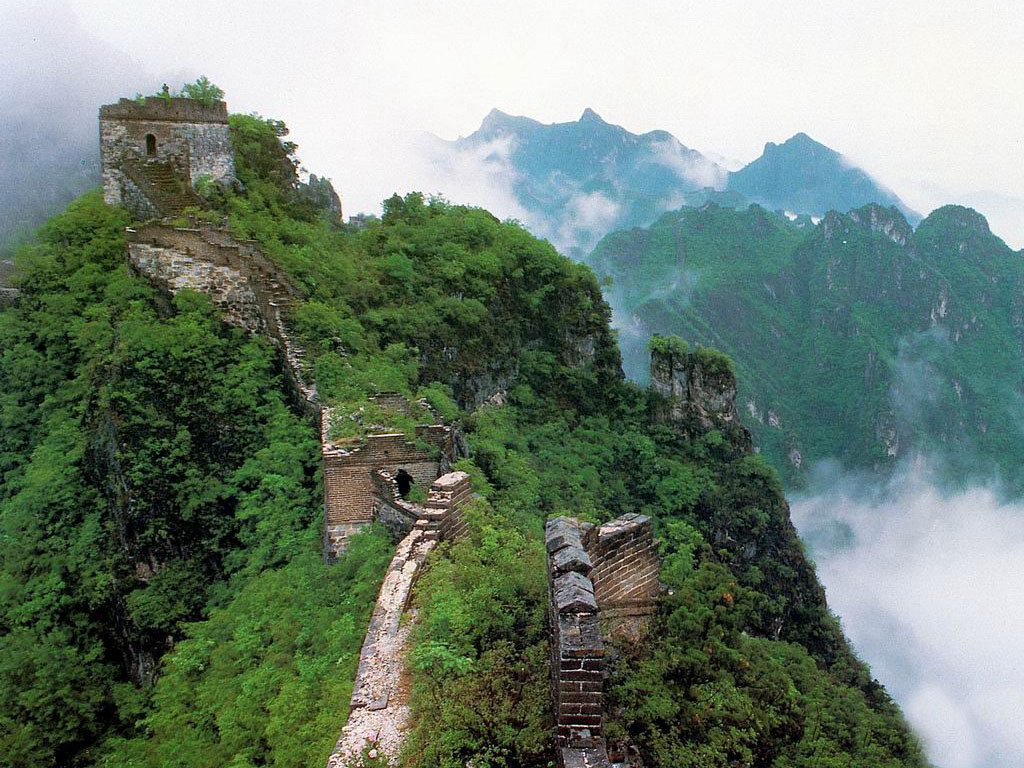
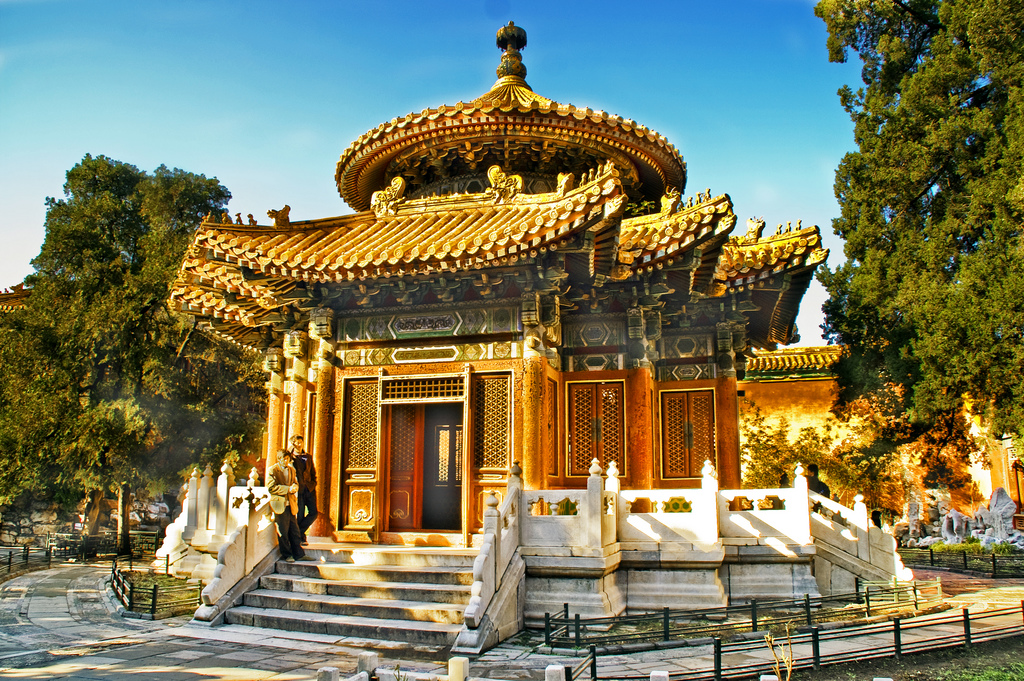
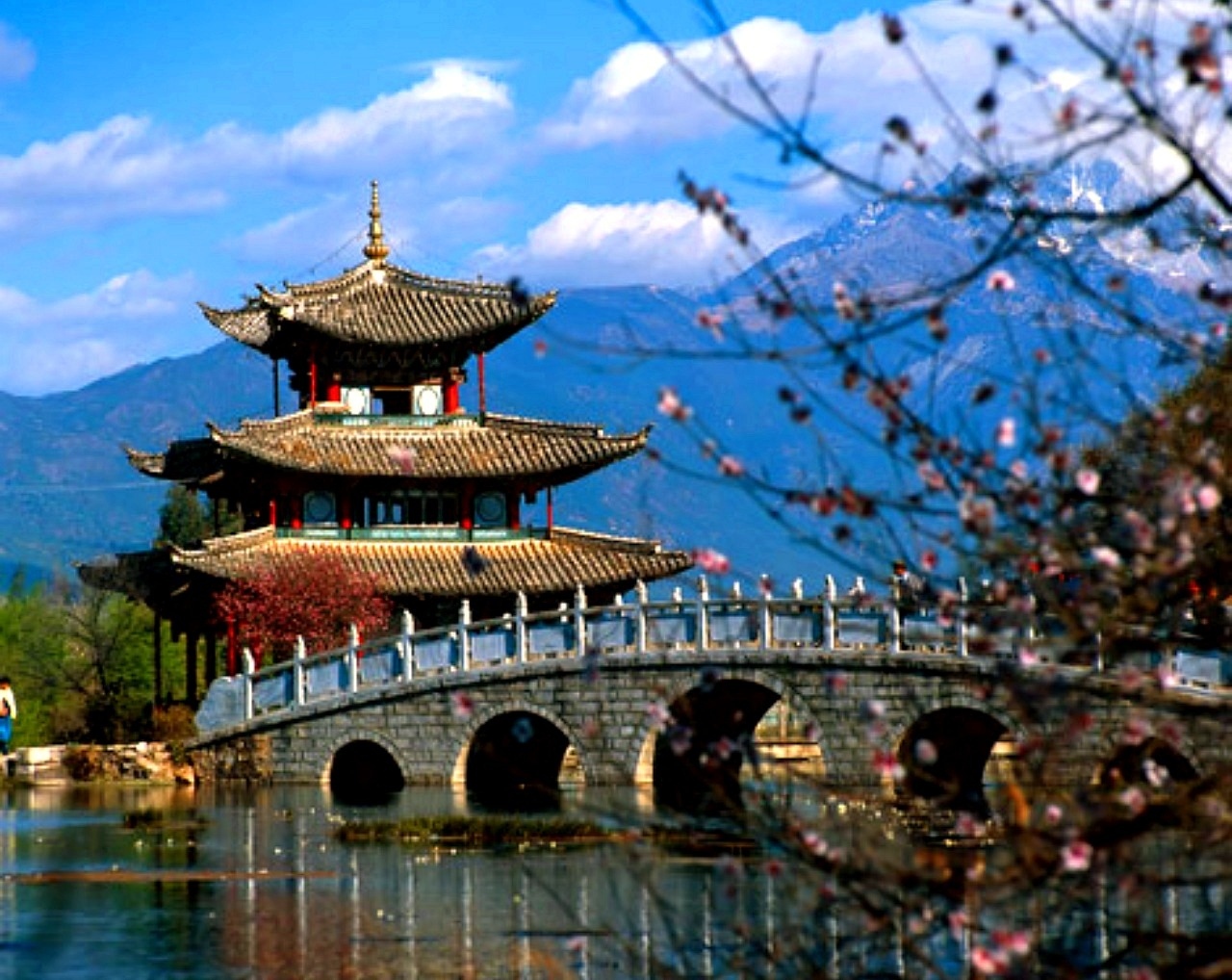
China is a wonderful country which harmoniously combines beautiful nature, grand architecture, ancient traditions and bustle of modern life. It does not matter how you will decide to start your acquaintance with China, the journey will be fantastic anyway. In Beijing you can see the Forbidden City, a stunning imperial palace built in the 15th century; visit the Temple of Heaven, where you can feel the cosmos energy and take a tai chi lesson; and watch charming giant pandas in Beijing Zoo. In Xian there is the famous Terracotta Army, hundreds of life-size models made to be buried with the First Emperor Qin in the 3rd century BC. In central Lhasa you can see the world’s highest ancient palace – the breathtaking Potala Palace, the former residence of the Dalai Lama, now a museum. Nature lovers will like the Yellow Mountains, a fabulous land of fancy pine-trees, rocks and mystical clouds; West Lake in Hangzhou, which is equally tremendous in all seasons; and the majestic Yangtze River, unhurriedly travelling through vast expanses of China.
China, the official name the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the most populous country in the world (over 1.35 billion people live in China); ranked third in the world in area after Russia and Canada (around 9.6 million square kilometers). China borders 14 states: Vietnam, Laos, Burma, India, Bhutan, Nepal, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan, Russia, Mongolia, and North Korea. The capital of China is Beijing. The official language is Standard Chinese, also known as Mandarin.
The national currency is the Renminbi (its basic unit is Yuan). Be prepared to pay mostly in cash, as credit cards are accepted in hotels, some restaurants and big stores or malls. ATMs are widely spread. You can exchange currency at the airport, banks and exchange offices.
China’s terrain consists of plains in the east, hills and low mountains in the south, large mountain ranges in the west and high plateaus in the north. Due to the country’s size the climate is very diverse – from tropical in the south to subarctic in the north.
Beijing Capital International Airport (PEK)
Guangzhou Baiyun International Airport (CAN)
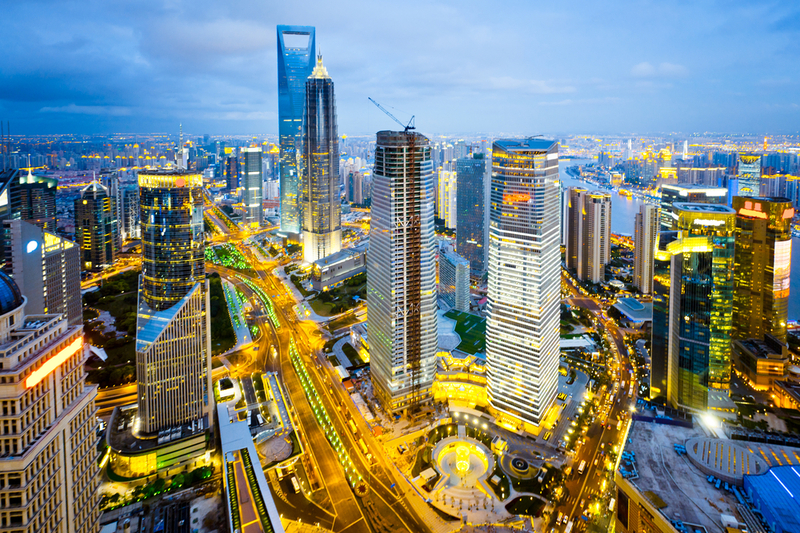
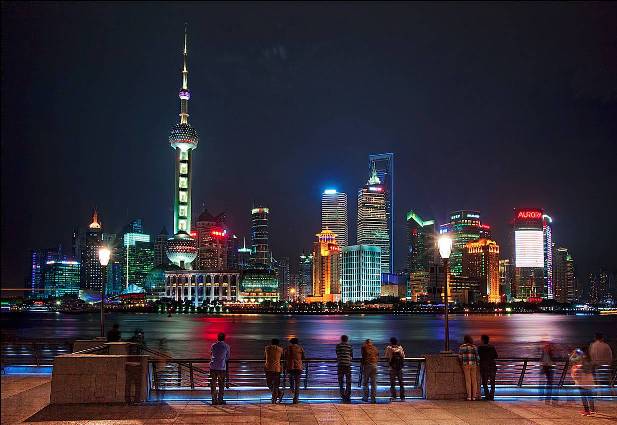
Shanghai Pudong International Airport (PVG)
Chengdu Shuangliu International Airport (CTU)
Shenzhen Bao'an International Airport (SZX)
Kunming Changshui International Airport (KMG)
Xi'an Xianyang International Airport (XIY)
Chongqing Jiangbei International Airport (CKG)
Hangzhou Xiaoshan International Airport (HGH)
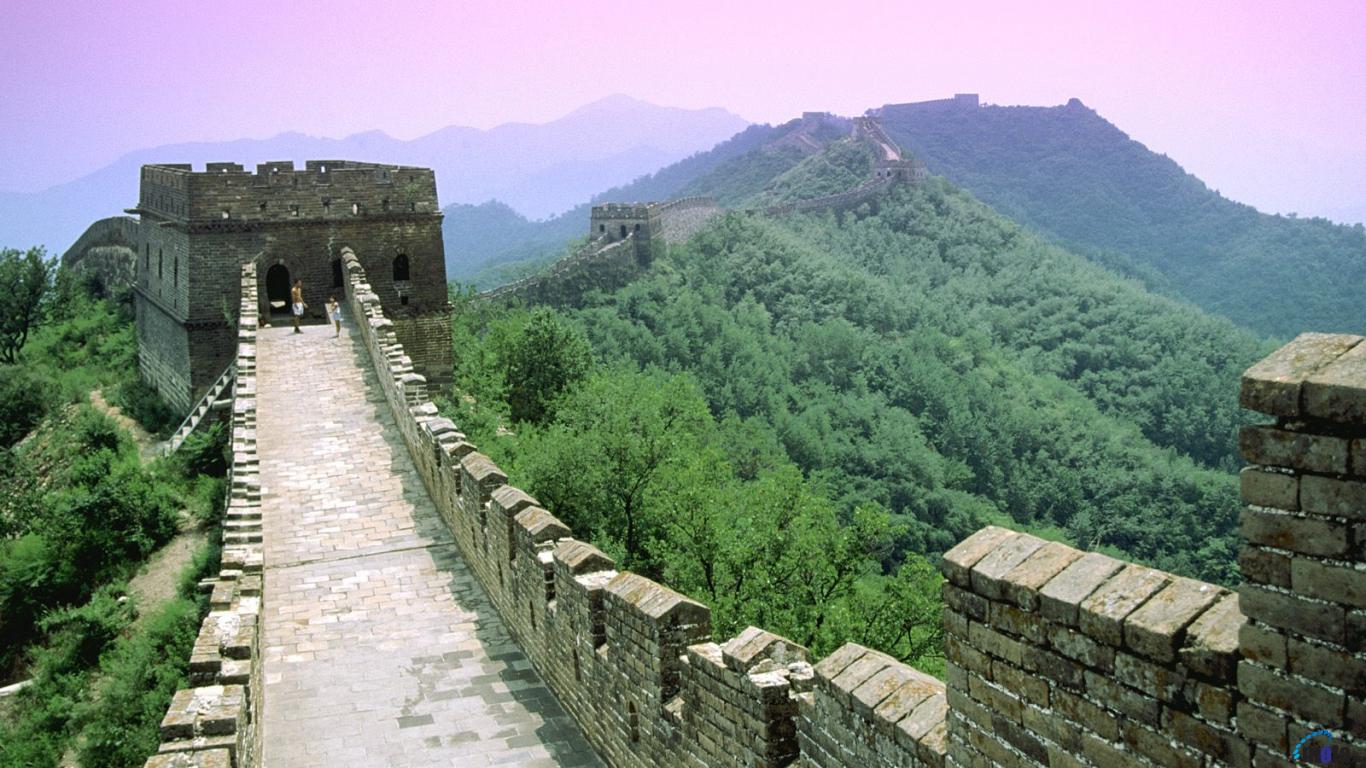
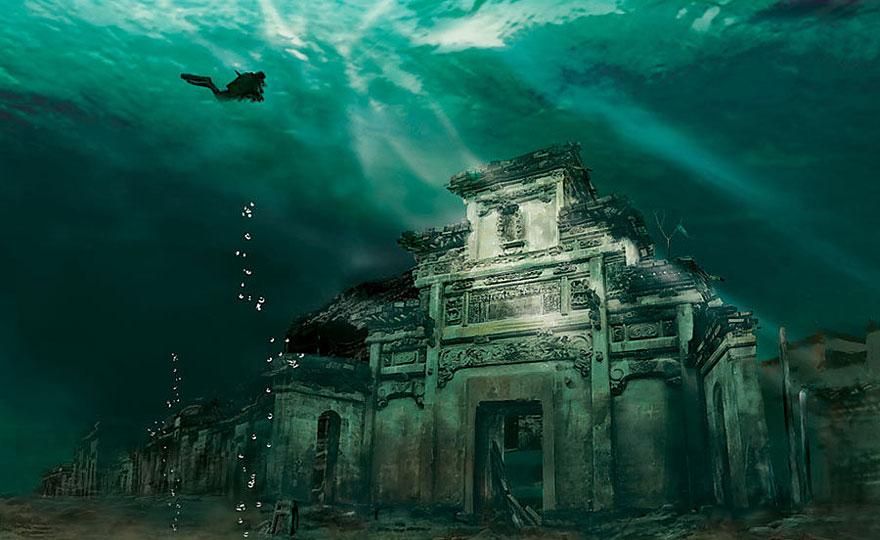
The Great Wall of China, which attracts so many tourists from all over the world, is also a fantastic diving site. In 1981 the Chinese government decided to flood some territory where the Great Wall ran, in order to resolve water shortages in Tian Jin, so part of the Wall is covered with 5-35 meters of water. While exploring the underwater wall you can find a gate to a tower and explore it from inside. The visibility is about 3-5 meters because of lots of algae and mud.
Another unforgettable diving site is the sunken Lion City at Qiandao Lake, Zhejiang Province. The city had been inhabited for 18 centuries until in 1959 the construction of a new hydroelectric power station began and it was decided to erect a dam. Lion City’s amazing white temples, paved roads, memorial arches, and houses went under water and created stunning diving place. The depth is from 26 to 40 meters.
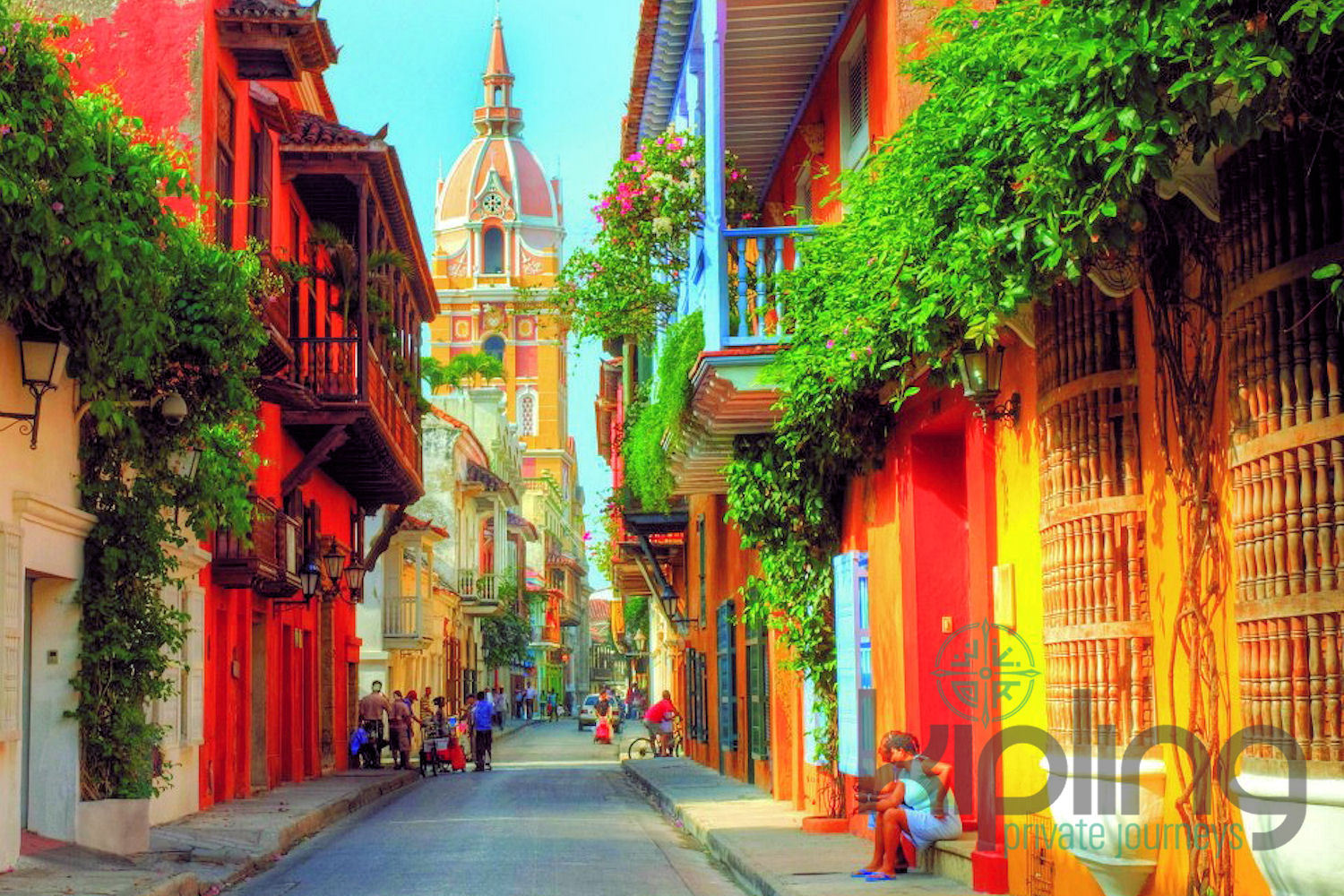
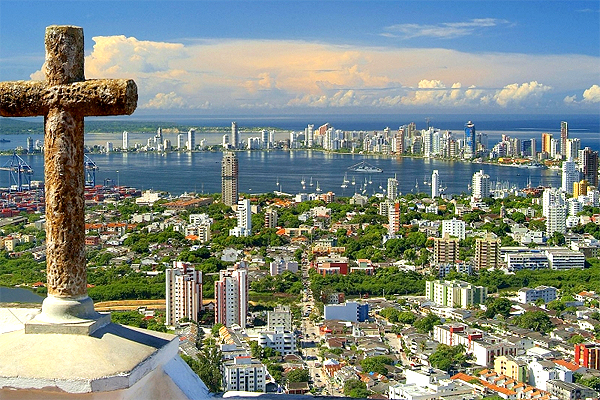
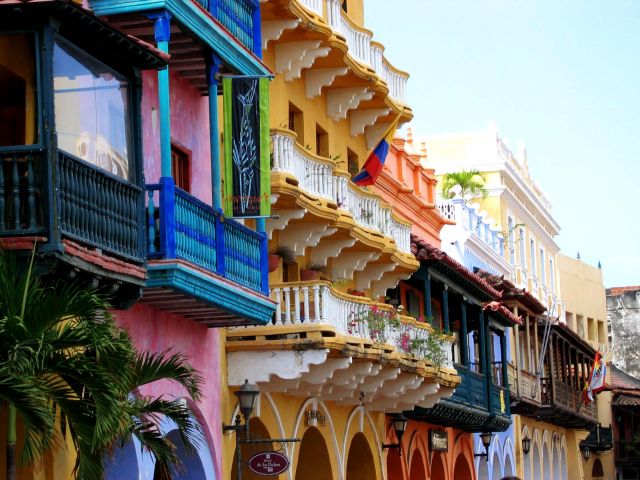
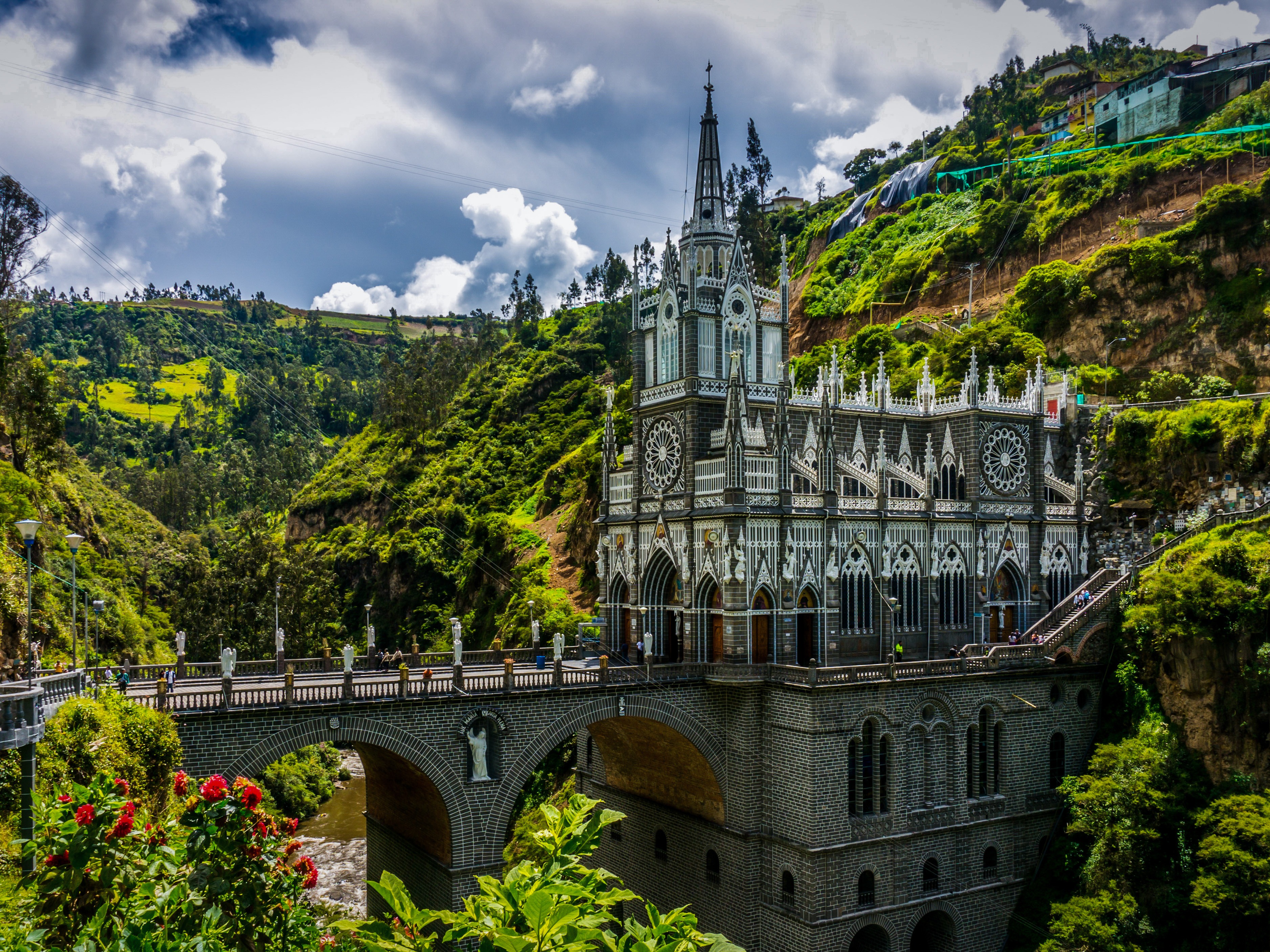
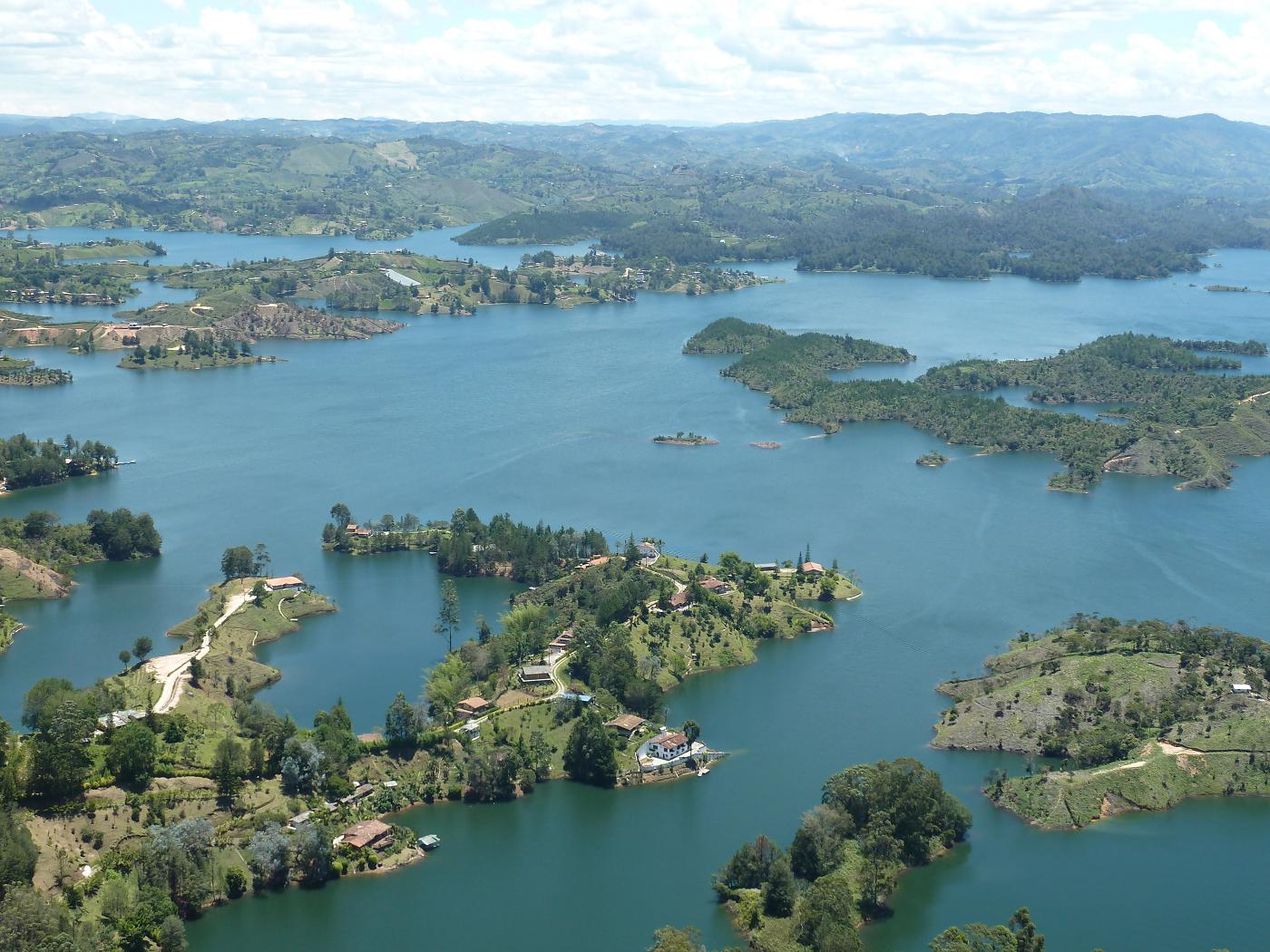
Colombia
What to see in Colombia? Cartagena and Bogota; Tayrona National Park; coffee plantations; humpback whales migration in Nuqui; Ciudad Perdida; wildlife of the Amazon River; San Andres and Providencia coral reef; Lake Toto; the Sebastian de Belcazar wreck; and coral gardens of Taganga.
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country situated in the northwest of South America. It has borders with Panama, Ecuador, Venezuela, Brazil and Peru, and is washed by the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean. The capital of the country is Bogotá. The official language is Spanish. The total area of the country is about 1.1 million square kilometers; the population is approximately 48 million people.
Colombia has a great diversity of landscapes and climate zones, so if you plan to travel extensively, be ready to take many different clothes.
The national currency is the Colombian peso. It is recommended to exchange currency only at hotels, banks and exchange offices. Visa and MasterCard are widely accepted. In all the main cities there are ATMs.
Colombia is able to satisfy a broad spectrum of tastes. Those who prefer relaxed sunbathing can go to secluded beaches of Tayrona National Park or bask on the coasts of San Andres and Providencia. Connoisseurs of colonial architecture will like picturesque buildings of Cartagena and Bogota, not to mention their interesting museums and delicious local food. Those who want to to get the real taste of Colombia can visit small pueblos in the coffee region. From July to October nature lovers can watch humpback whales coming close to the shore at Nuqui, on Colombia’s Pacific Coast. While travelling along the Amazon River you will be able to visit indigenous communities and see various exotic animals. Or you can take a jungle trek from Santa Marta or Taganga to Ciudad Perdida (The Lost City) and get a great adventure of your life. Those who are fond of extreme will also like San Gil, which offers a lot of opportunities for paragliding, whitewater rafting, and mountain biking and other adventure sports.
El Dorado International Airport (BOG), the main international airport in Colombia, situated in Bogotá.
José María Córdova International Airport (MDE), the second biggest airport in Colombia, situated in the city of Rionegro.
Alfonso Bonilla Aragón International Airport (CLO), located in Palmira.
Rafael Núñez International Airport (CTG), the largest airport in the northern Caribbean region.
Ernesto Cortissoz International Airport (BAQ) serves the area of Barranquilla.
Palonegro International Airport (BGA)
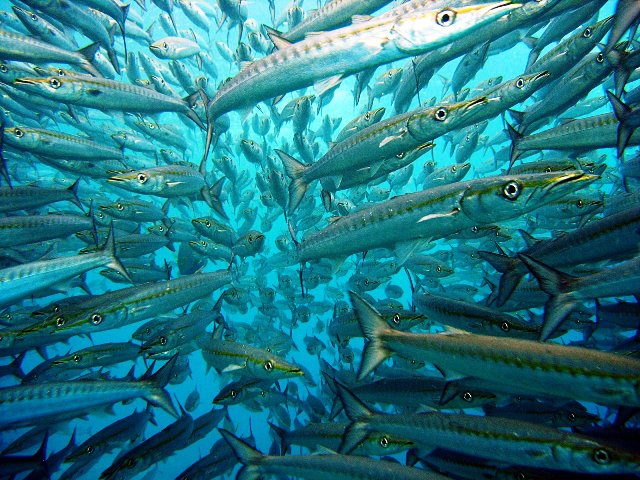
Colombia is a popular destination for scuba divers, because it is the only country in South America which has both Pacific and Caribbean coastlines.
On the Caribbean side the most popular diving places include Capurgana, Golfo de Morrosquillo (near Tolu), Islas del Rosario (Cartagena), and Taganga (coral gardens and tropical reef fish, including angelfish, butterfly fish, yellowtail snapper, and green moray eels) and San Andres and Providencia. Off the archipelago of San Andres and Providencia divers can see the world’s third largest coral reef, inhabited by numerous marine creatures. The water temperature is very comfortable and the visibility is up to 40 meters.
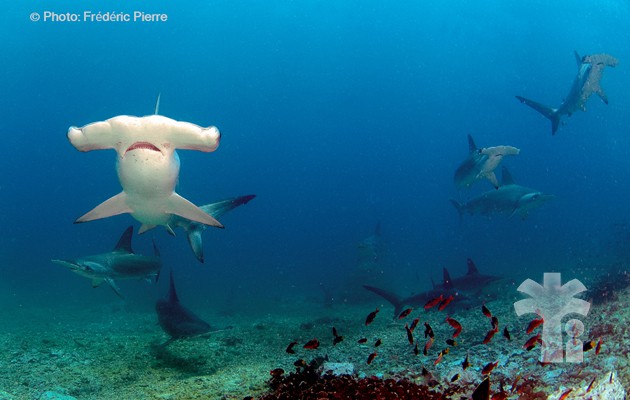
Off the Pacific coast the most famous sites are Cali, Gorgona Island (turtles, white-tip reef sharks, groupers, mantas, whalesharks, and, from June to October, humpback whales) and MalpeloCongo (Brazzaville)
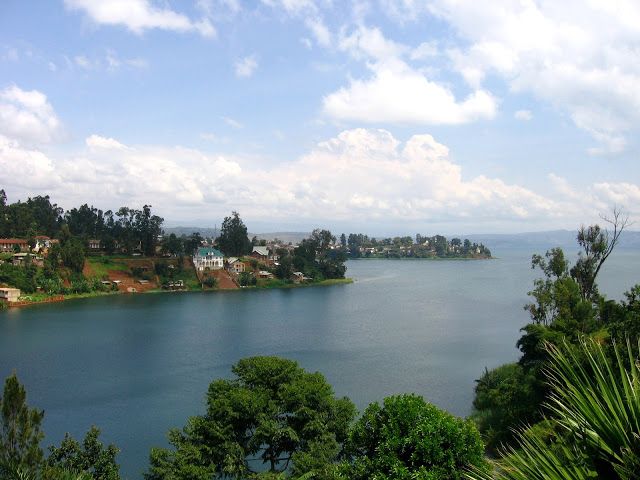
The Republic of the Congo (French: République du Congo), also known as the Congo Republic,[5] West Congo, Congo-Brazzaville or simply Congo, is a country located in Central Africa. It is bordered by five countries: Gabon and the Atlantic Ocean to the west; Cameroon to the northwest; the Central African Republic to the northeast; the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the east and south; and the Angolan exclave of Cabinda to the southwest.
The region was dominated by Bantu-speaking tribes, who built trade links leading into the Congo River basin. Congo-Brazzaville was formerly part of the French colony of Equatorial Africa.[1] Upon independence in 1960, the former colony of French Congo became the Republic of the Congo. The People's Republic of the Congo was a Marxist–Leninist one-party state from 1970 to 1991. Multi-party elections have been held since 1992, although a democratically elected government was ousted in the 1997 Republic of the Congo Civil War and President Denis Sassou Nguesso has ruled for 26 of the past 36 years.
The political stability and development of hydrocarbon production made the Republic of the Congo the fourth largest oil producer in the Gulf of Guinea, providing the country with relative prosperity despite instability in some areas and unequal distribution of oil revenue nationwide.
The Republic of the Congo (French: République du Congo), also known as the Congo Republic,[5] West Congo, Congo-Brazzaville or simply Congo, is a country located in Central Africa. It is bordered by five countries: Gabon and the Atlantic Ocean to the west; Cameroon to the northwest; the Central African Republic to the northeast; the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the east and south; and the Angolan exclave of Cabinda to the southwest.
The region was dominated by Bantu-speaking tribes, who built trade links leading into the Congo River basin. Congo-Brazzaville was formerly part of the French colony of Equatorial Africa.[1] Upon independence in 1960, the former colony of French Congo became the Republic of the Congo. The People's Republic of the Congo was a Marxist–Leninist one-party state from 1970 to 1991. Multi-party elections have been held since 1992, although a democratically elected government was ousted in the 1997 Republic of the Congo Civil War and President Denis Sassou Nguesso has ruled for 26 of the past 36 years.
The political stability and development of hydrocarbon production made the Republic of the Congo the fourth largest oil producer in the Gulf of Guinea, providing the country with relative prosperity despite instability in some areas and unequal distribution of oil revenue nationwide.
Transport in the Republic of the Congo includes land, air and water transportation. The country's rail system was built by forced laborers during the 1930s and largely remains in operation. There are also over 1000 km of paved roads and two major international airports (Maya-Maya Airport and Pointe Noire Airport) which have flights to destinations in Europe, Africa, and the Middle East. The country also has a large port on the Atlantic Ocean at Pointe-Noire and others along the Congo River at Brazzaville and Impfondo.
When to scuba dive in the Republic of the Congo:Water temperature stays above 20C all year on average.Local standards for gear:The best scuba diving spots in the Republic of the Congo:The best spots to snorkel in the Republic of the Congo:Fun scuba Facts:Country data:Administrative detailsCurrency: Central African franc (XAF)Population: is about 4,000,000 (2009)Time Zone: WAT (GMT+1)Main languages spoke: French, Kongo/Kituba, Lingala ## Diveable overseas territories:Congolese Island diving federations:Local diving laws and regulations (and PADI-equivalent certifications)
Congo (Kinshasa)
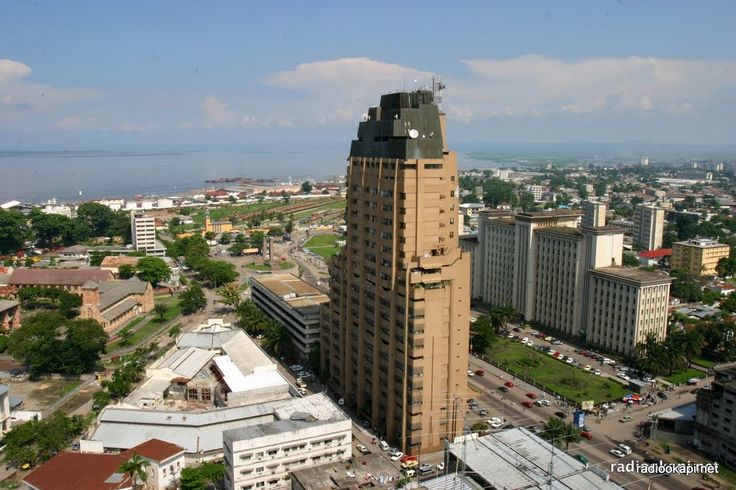
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (/ˈkɒŋɡoʊ/; French pronunciation: [kɔ̃ɡo]; French: République démocratique du Congo), also known as DR Congo, DRC, DROC, East Congo, Congo-Kinshasa, or simply the Congo[6][7] is a country located in Central Africa. The DRC borders the Central African Republic, and South Sudan to the north; Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi and Tanzania to the east; Zambia and Angola to the south; the Republic of the Congo to the west and the Atlantic Ocean to the southwest. It is the second-largest country in Africa by area and eleventh largest in the world. With a population of over 80 million,[1] the Democratic Republic of the Congo is the most populated officially Francophone country, the fourth most-populated nation in Africa and the eighteenth most populated country in the world.
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (/ˈkɒŋɡoʊ/; French pronunciation: [kɔ̃ɡo]; French: République démocratique du Congo), also known as DR Congo, DRC, DROC, East Congo, Congo-Kinshasa, or simply the Congo[6][7] is a country located in Central Africa. The DRC borders the Central African Republic, and South Sudan to the north; Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi and Tanzania to the east; Zambia and Angola to the south; the Republic of the Congo to the west and the Atlantic Ocean to the southwest. It is the second-largest country in Africa by area and eleventh largest in the world. With a population of over 80 million,[1] the Democratic Republic of the Congo is the most populated officially Francophone country, the fourth most-populated nation in Africa and the eighteenth most populated country in the world.
The territory of the DR Congo was first settled about 80,000 years ago. The Bantu migration began in the 7th century. The Kingdom of Kongo ruled from the 14th to 19th centuries. By 1879, Belgian colonization began leading to the establishment of the Congo Free State in 1885. In 1908, Belgium annexed the country which then became the Belgian Congo. During the Congo crisis, Belgium granted its independence in 1960 and in 1965, Mobutu Sese Seko came into power, renaming the country Zaire in 1971. By the early 1990s, Mobutu's regime began to weaken. The Congolese Civil Wars, which began in 1996, brought about the end of Mobutu's 32-year reign[1] and devastated the country. These wars ultimately involved nine African nations, multiple groups of UN peacekeepers and twenty armed groups,[8][9][unreliable source?] resulting in the deaths of 5.4 million people.[10][11][12][13]
The Democratic Republic of Congo is extremely rich in natural resources, but is politically unstable, has a lack of infrastructure, deep rooted corruption, and centuries of both commercial and colonial extraction and exploitation with little holistic development. Besides the capital, Kinshasa, the other major cities, Lubumbashi and Mbuji-Mayi, are both mining communities. DR Congo's largest export is raw minerals, with China accepting over 50% of DRC's exports in 2012. As of 2015, according to the Human Development Index (HDI), DR Congo has a low level of human development, ranking 176 out of 187 countries.[5]
As of June 2016, DR Congo had one major national airline (Congo Airways) that offered flights inside DR Congo. Congo Airways was based at Kinshasa's international airport. All air carriers certified by the DRC have been banned from European Union airports by the European Commission, due to inadequate safety standards.[111]
Several international airlines service Kinshasa's international airport and a few also offer international flights to Lubumbashi International Airport.
The diving industry is undeveloped across both Congos, and several unique considerations exist for those wishing to do some scuba in the region. Most of the Great Lakes have a build-up of methane in the water from volcanic activity, and Lake Albert is home to a huge variety of hippos - not your friendliest diving partners. The Congo River has very little visibility, even in the Mangroves Park where one might hope to see a manatee. Lac Mai Ndombe is pitch-black.
The best option for diving would be in Lake Tanganyika, from Kalemie. Some small diving operations exist here for the purpose of collecting exotic fish - don’t count on them assisting your own diving excursions in any way.
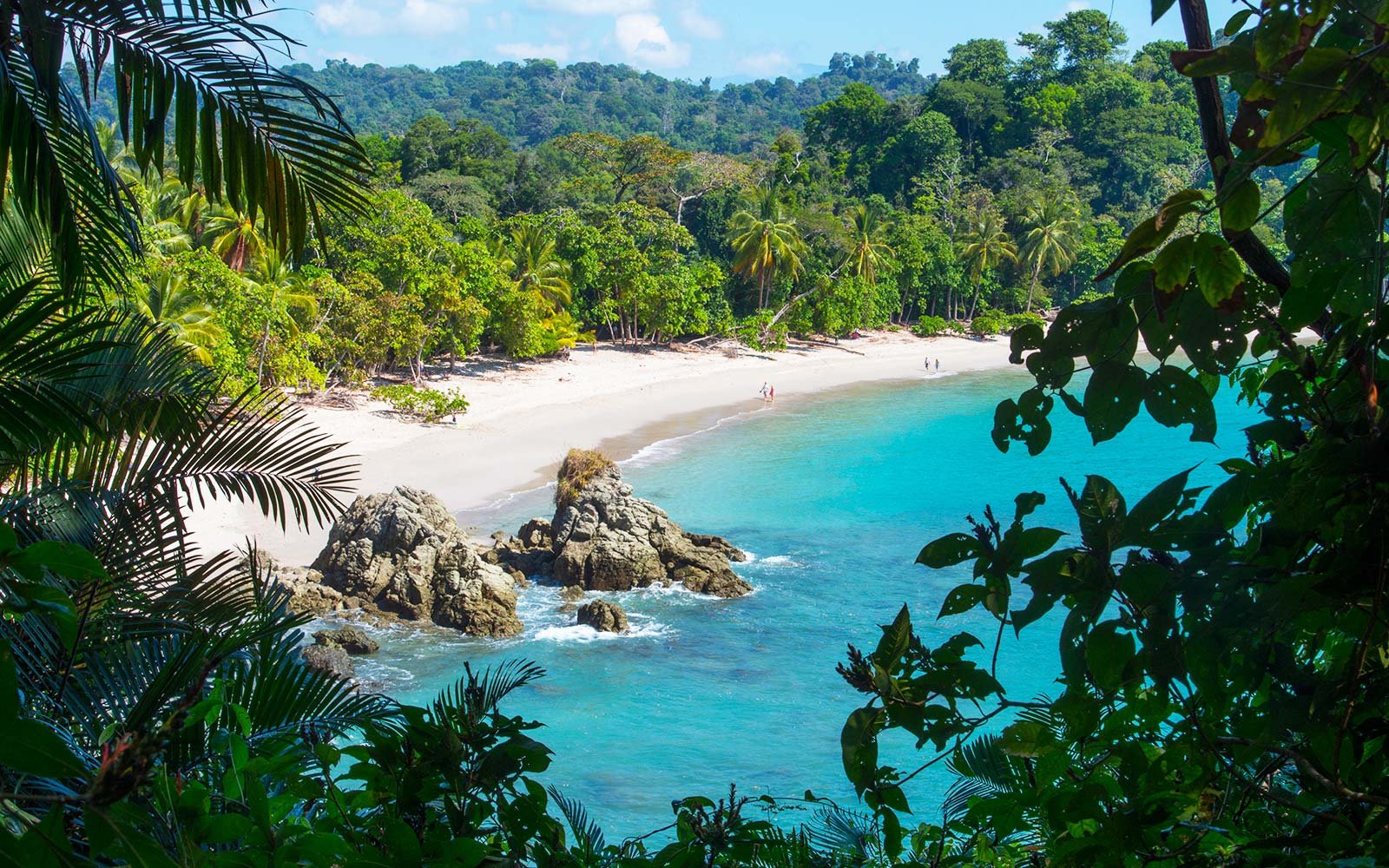
Costa Rica
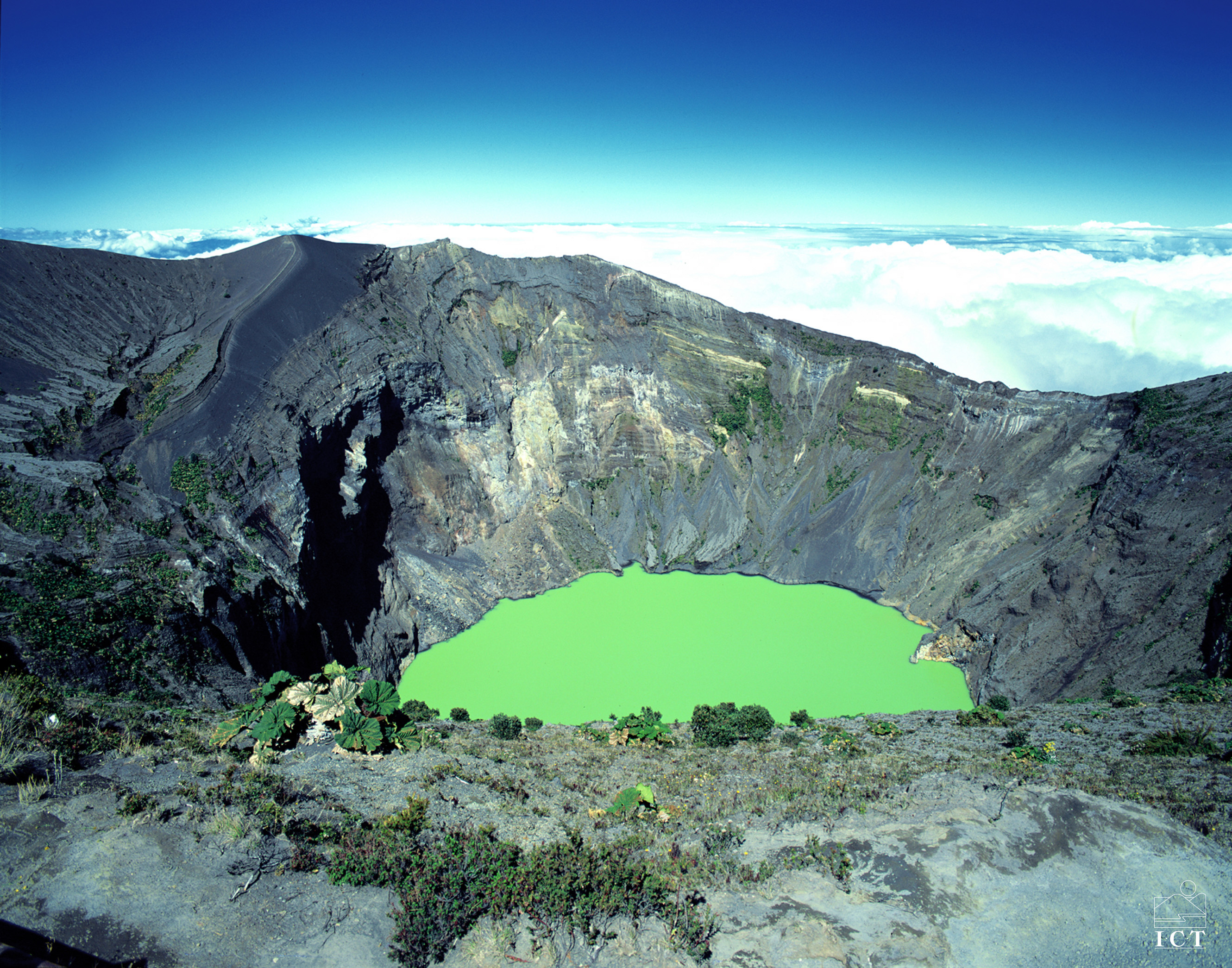
What to see in Costa Rica? La Amistad park; volcanoes Poas and Irazu; Caño Negro and Isla Bolaños; Tortuga; marine life of Coco Island; Playa Flamingo, Playa La Pinta, Nosara and Playa Hunkiyal; Cahuita reef; and bull sharks of Beth Island.
Costa Rica is a state in Central America. Its eastern shores are washed by the Caribbean Sea, and the southern and western – by the Pacific Ocean. The nearest neighbors are the Republic of Panama and Nicaragua. Lion's share of the land is covered with lush tropical forests, which produce valuable timbers. The climate of Costa Rica is subequatorial, due to rough terrain and climatic conditions climate conditions in the regions differ greatly. The capital is San Jose.
Costa Rica is rich in attractions that can satisfy any tourist. Here there is the famous international park La Amistad, visiting of which can make happy anyone. Near the capital, in the town of Alajuela, you can visit Juan Santamaria Museum, the Zoo, as well as admire the Poas Volcano. You can also visit the active volcano Irazu near Cartago, near which there is the National Park. In La Guasima you can see the world's largest butterfly farm. Coffee lovers will enjoy trips to the Coffee Museum and the Coffee Institute of San Pedro de Barva, Heredia. Tourists, interested in the cultural heritage of the country, can visit the Museum of History of Religion and Antiquities in Orosi.
Those who are fond of nature will like nature reserves – national wildlife refugesCaño Negro and Isla Bolaños and forest reserve Santa Elena, biological reserve Carara and many others. Also it is worth visiting the luxurious Costa Rican waterfalls of San Rafael, La Paz and Catarata de la Fortuna, and highlight of Costa Rica - the famous "turtle" island of Tortuga.
The national currency is the Costa Rican Colon, but according a good old touristic tradition US dollars are also widespread here.
International airports in Costa Rica
In Costa Rica, four airports have international status, but two of them are the main- Juan Santamaria and Daniel Oduber Quirós.
• Daniel Oduber Quiros International Airport (LIR)
Located in Guanacaste.
• Juan Santamaria International Airport (SJO)
Located in the capital of the state and has the status of the most popular and busiest airport in the country.
• Tobias Bolanos International Airport (SYQ)
• Pablo Zidar International Airport (LIO)
Located in Puerto Limon, Province of Limon. It is also known as Limon International Airport.
Diving in Costa Rica
Diving in Costa Rica, according to the most experienced "sea dogs", is the most fascinating among many Caribbean countries. The warm climate, constant temperature of clean water and diverse underwater world already provide the country with stable popularity among fans of diving, but the real highlights of Costa Rica are hard-to-reach Isla del Coco and Coco Island, also known as Coconut Island - the world’s largest uninhabited island. Coco Island is surrounded by many myths, which makes its halo glow even brighter. There are rumors that Coconut became the prototype of the famous "Jurassic Park" by Spielberg and "Treasure Island" by R.L. Stevenson; and the respected underwater explorer Jacques Cousteau awarded Coconut with the title of "most beautiful island" in the world. Also, they say that on Coco Island gold of the Incas was buried, which has been worrying adventurers’ hearts for many centuries. No wonder that after so many legends glorifying the unusual island, Costa Rica is flooded with lots of divers who want to see these miracles with their own eyes, or rather, to feel all its marvels in diving.
The underwater fauna off the coast of Coco Island strikes by extraordinary diversity. Here you can find such fish as hammerhead sharks, giant manta rays, grayfin jewfish and whitetip reef sharks, marlins, tunas and sardines. The coral thickets are inhabited by eels, sea turtles, octopuses and parrot fish. Sometimes you can see dolphins or not too sociable whales. Due to the unique ecosystem Coconut Island is included in the list of world heritage of humanity.
It is worth noting that, despite the excellent visibility of water, strength and direction of coastal currents can change in just a few moments, so diving here is recommended only for experienced divers.
Divers also like such places as Playa Flamingo, Playa La Pinta, Nosara and Playa Hunkiyal. You will also like Bahia Drake, Marine National Park Ballena, famous coral reef in Cahuita, which is part of the National Park and the island Beth, where you can meet massive bull sharks and flying rays.
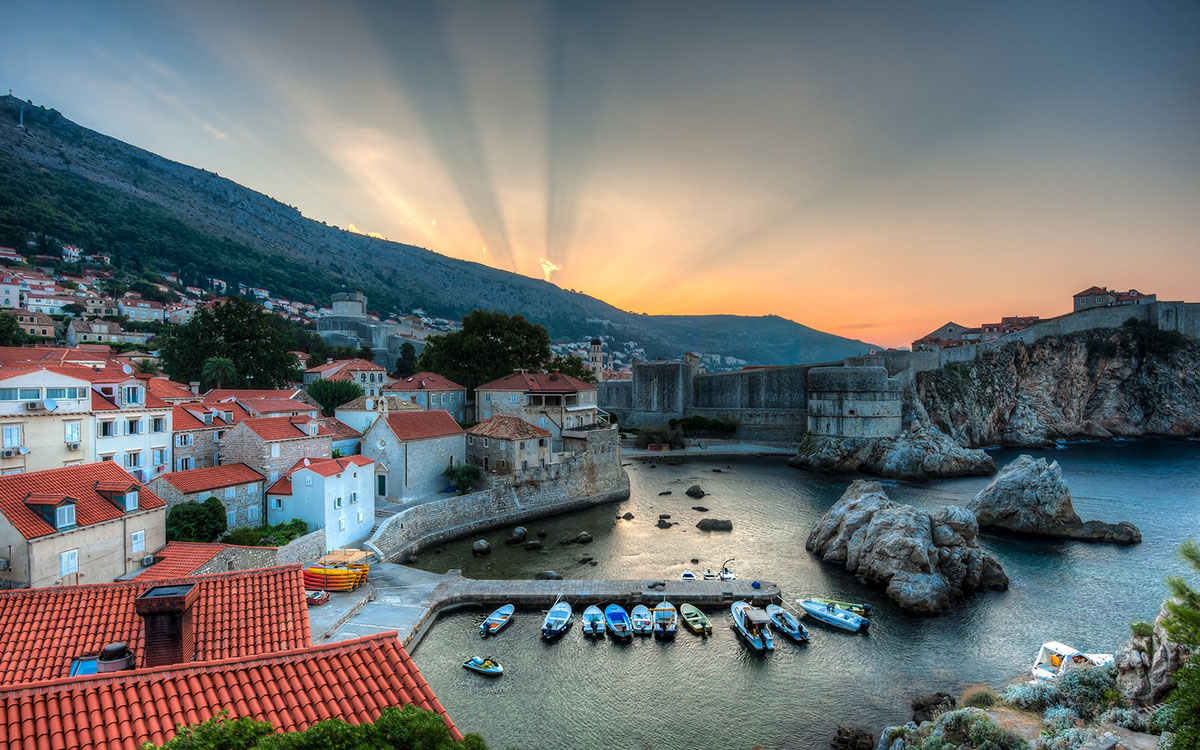
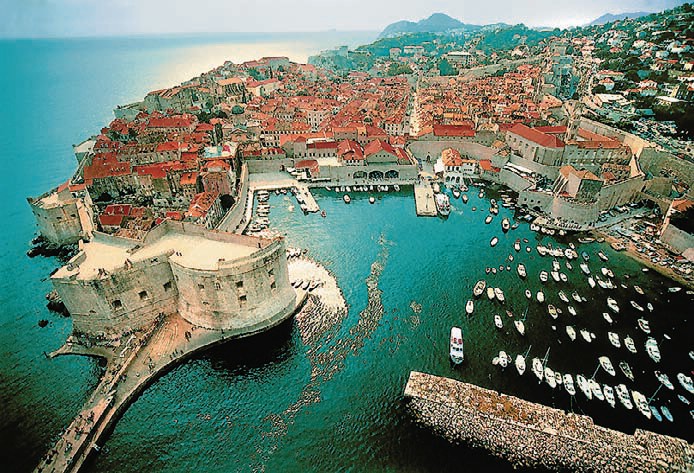
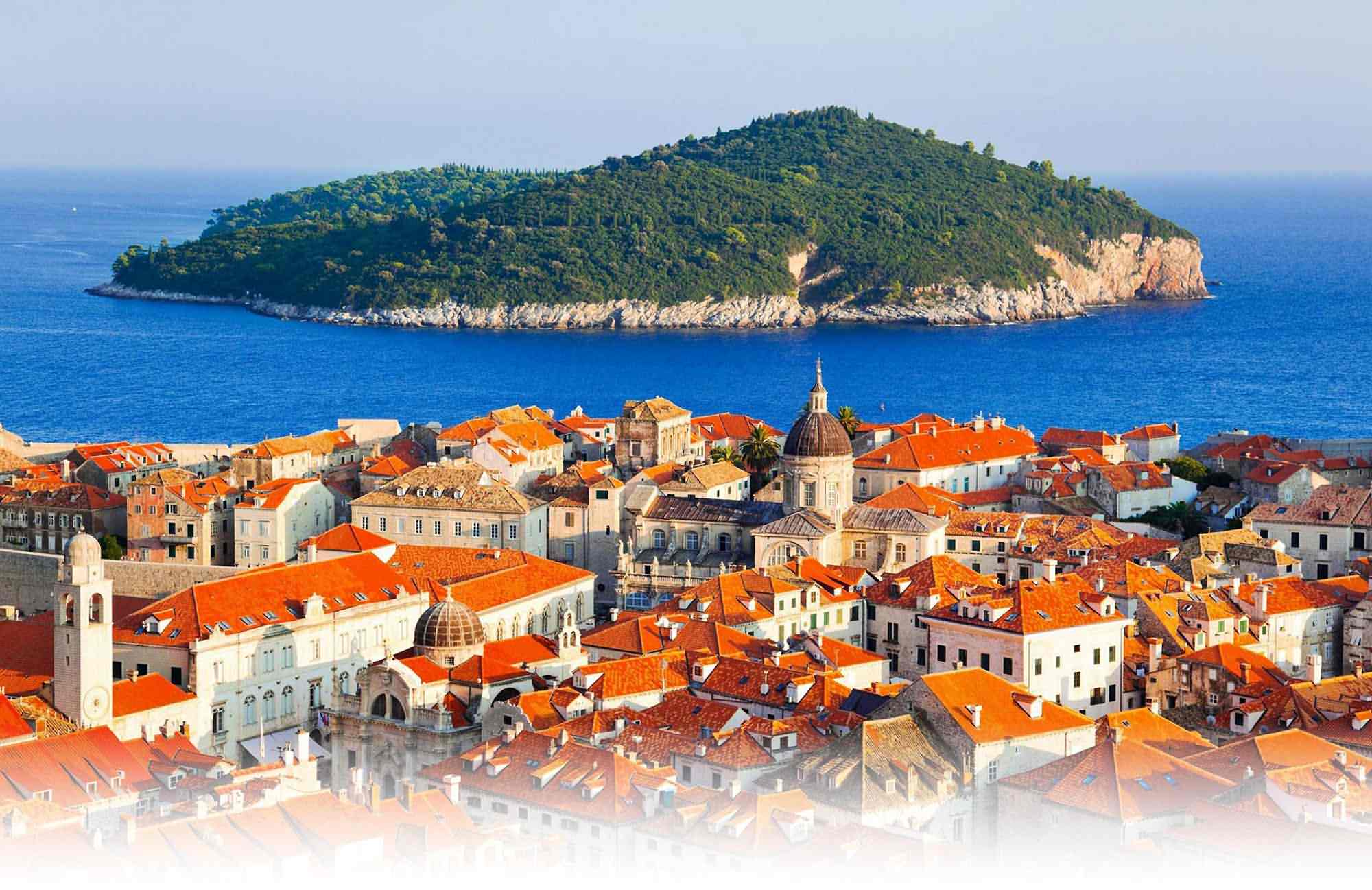
Croatia
Amphitheater of Pula, Diocletian's Palace in Split, Princely Palace in Dubrovnik, Brijuni - a group of islands in front of the western coast of Istria. In the western area of the Croatian city of Pula there is a Roman forum. Krka National Park is the seven beautiful cascades of waterfalls, two ancient monasteries, amazingly picturesque landscapes and a sense of unity with nature.
Croatia officially the Republic of Croatia is a sovereign state between Central Europe, Southeast Europe, and the Mediterranean. Its capital city is Zagreb, which forms one of the country's primary subdivisions, along with its twenty counties. Croatia covers 56,594 square kilometres (21,851 square miles) and has diverse, mostly continental and Mediterranean climates. Croatia's Adriatic Sea coast contains more than a thousand islands. The country's population is 4.28 million, most of whom are Croats, with the most common religious denomination being Roman Catholicism.
A unitary state, Croatia is a republic governed under a parliamentary system. The International Monetary Fund classified Croatia as an emerging and developing economy, and the World Bank identified it as a high-income economy. Croatia is a member of the European Union (EU), United Nations (UN), the Council of Europe, NATO, the World Trade Organization (WTO) and a founding member of the Union for the Mediterranean. As an active participant in the UN peacekeeping forces, Croatia has contributed troops to the NATO-led mission in Afghanistan and took a non-permanent seat on the UN Security Council for the 2008–2009 term.
Travel to any destination may be adversely affected by conditions including (but not limited) to security, entry and exit requirements, health conditions, local laws and culture, natural disasters and climate. Regardless of your destination, check your local travel advisory board or department for travel advice about that location when planning your trip and again shortly before you leave.
Language – Croatian, with English widely spoken in tourist areas.
Currency – Kuna (and the Euro). Credit cards are widely accepted.
Major Airports – Dubrovnik (DBV), Split (SPU) and Zadar (ZAD)
Electricity and Internet – Electricity is 220 volts, 50 Hz. Internet service is available in most of the hotels and cafes.
| Rank | Airport | City | IATA / ICAO | 2015 | 2016 | Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Zagreb Airport | Zagreb | ZAG / LDZA | 2,587,798 | 2,776,087 |  6.9% 6.9% |
| 2. | Split Airport | Split | SPU / LDSP | 1,955,400 | 2,289,987 |  11.5% 11.5% |
| 3. | Dubrovnik Airport | Dubrovnik | DBV / LDDU | 1,693,934 | 1,993,243 |  17.6% 17.6% |
| 4. | Zadar Airport | Zadar | ZAD / LDZD | 487,652 | 520,924 |  6.7% 6.7% |
| 5. | Pula Airport | Pula | PUY / LDPL | 359,426 | 436,121 |  10.7% 10.7% |
| 6. | Rijeka Airport | Rijeka | RJK / LDRI | 139,718 | 145,297 |  4.0% 4.0% |
| 7. | Osijek Airport | Osijek | OSI / LDOS | 28,651 | 30,605 |  6.3% 6.3% |
| 8. | Brač Airport | Brač | BWK / LDSB | 8,809 | 12,354 |  28.7% 28.7% |
| TOTAL | 7,255,234 | 8,219,321 |  21.1% 21.1% | |||
Croatia lays claim to the lion’s share of the eastern Adriatic coast, and a quick look at a map will delight divers and reveal a land with more than its fair share of islands and coastline. To the north, situated at the foothills of the Alp and Dinarid mountain chains, Kvarner is one of the most beautiful gulfs on the Adriatic. It’s the closest warm water diving destination to Eastern Europe and diving is possible all year. Kvarner's underwater world is known for amazing wall dives and rocky reefs covered with beautiful gorgonians. The craggy coastline and relatively shallow water underpin an underwater world with enough variety to make this a great dive destination. Further south, the island of Vis is literally encircled with dive sites. From walls to wrecks to rocky reefs, there’s something here for divers of all levels.
Great Dives
- Plic Tenki – A wall here drops to 22 metres/72 feet and one of the most interesting sections is a rock pinnacle at about 15 metres/50 feet. Pockmarked with holes, this area is covered with underwater plant species and fish, such as two banded bream and scorpionfish. More experienced divers will enjoy the deeper part of the reef at 25-40 metres/82-130 feet, which is covered with red gorgonians.
- The Wreck of the Teti – Just off the Island of Mali Barjak, the bow of the 70-metre/230-foot long Teti is 7 metres/23 feet deep and the stern is at more than 30 metres/100 feet. Look for the conger eels here that are well used to divers.
- Bisevo Grotto – Blue Grotto is a magical sea cave and a prime dive site with visibility often better than 25 metres/80 feet. On the dive you’ll likely meet up with octopus, scorpionfish, lobster and more.
- The Cathedral – Not far from Zadar, off the small island of Premuda, is a dive site with a series of inter-connected caves through which sunlight filters in a spectacular display. Octopus and spider crabs reside here.
- Kornati Archipelago – There’s a wall off Rasip Island, festooned with sponges and corals, that drops to more than 60 metres/185 feet. Fish life is remarkable at recreational diving depths.
- Wreck of the Taranto – The Taranto is a fairly intact wreck of a merchant navy ship, which sank in 1943 after hitting a mine. Old tractors, part of the cargo, add interest to the dive, and large sea bass are sometimes spotted here.
Want to know more? Visit ScubaEarth® for further information on thousands of dive sites, marine species, destination essentials and more.
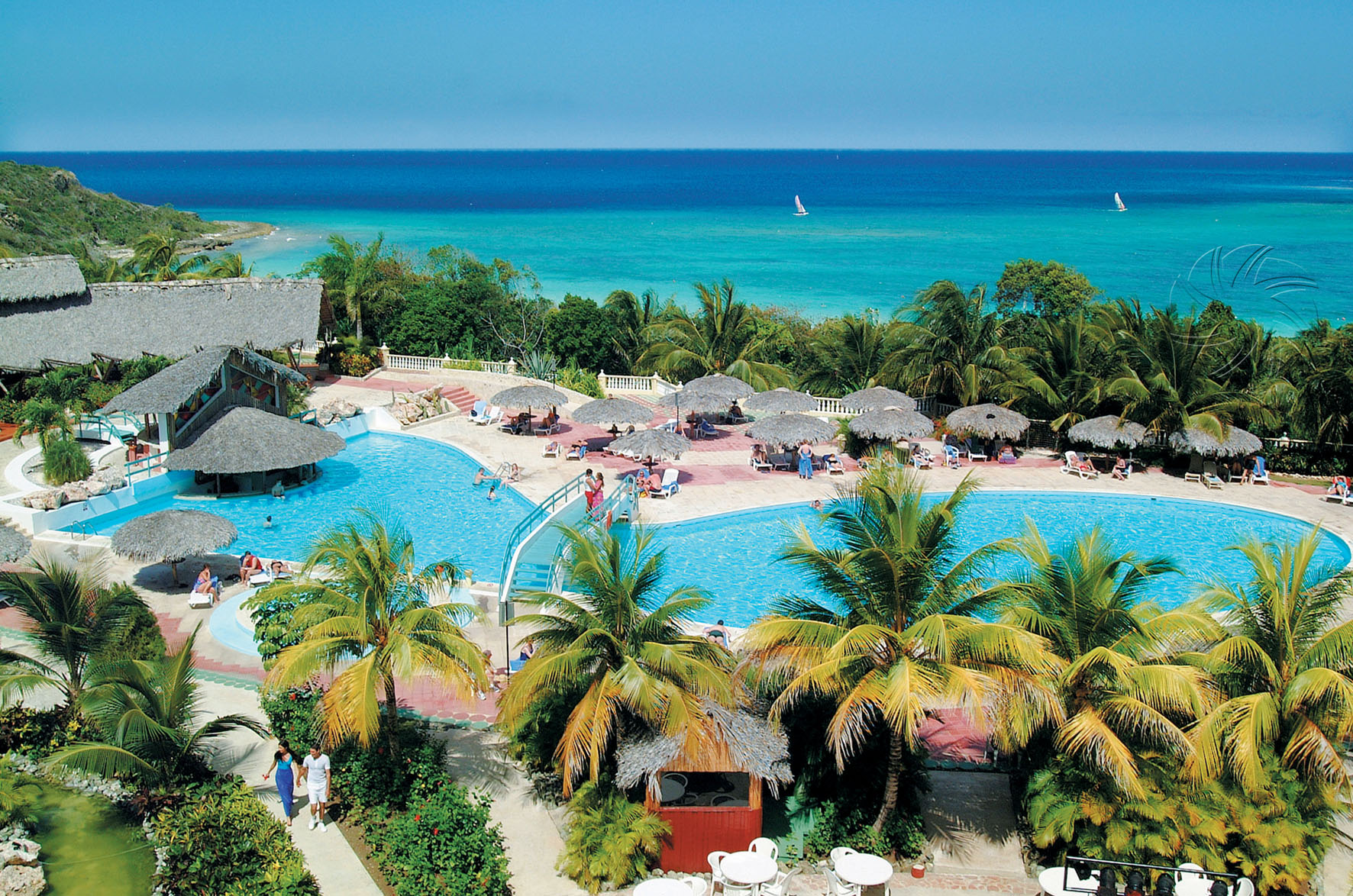
Cuba
Cuba, officially the Republic of Cuba República de Cuba , is a country comprising the island of Cuba as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located in the northern Caribbean where the Caribbean Sea, the Gulf of Mexico, and the Atlantic Ocean meet. It is south of both the U.S. state of Florida and the Bahamas, west of Haiti, and north of Jamaica. Havana is the largest city and capital; other major cities include Santiago de Cuba and Camagüey. Cuba is the largest island in the Caribbean, with an area of 109,884 square kilometres (42,426 sq mi), and the second-most populous after Hispaniola, with over 11 million inhabitants.
Cuba is an archipelago of islands located in the northern Caribbean Sea at the confluence with the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean. It lies between latitudes 19°and 24°N, and longitudes 74° and 85°W. The United States lies 150 kilometers (93 miles) across the Straits of Florida to the north and northwest (to the closest tip of Key West, Florida), and the Bahamas 21 km (13 mi) to the north. Mexico lies 210 kilometers (130 miles) across the Yucatán Channel to the west (to the closest tip of Cabo Catoche in the State of Quintana Roo).
Haiti is 77 km (48 mi) to the east, Jamaica (140 km/87 mi) and the Cayman Islands to the south. Cuba is the principal island, surrounded by four smaller groups of islands: the Colorados Archipelago on the northwestern coast, the Sabana-Camagüey Archipelago on the north-central Atlantic coast, the Jardines de la Reina on the south-central coast and the Canarreos Archipelago on the southwestern coast.
Sierra MaestraThe main island, named Cuba, is 1,250 km (780 mi) long, constituting most of the nation's land area (104,556 km2 (40,369 sq mi)) and is the largest island in the Caribbean and 17th-largest island in the world by land area. The main island consists mostly of flat to rolling plains apart from the Sierra Maestra mountains in the southeast, whose highest point is Pico Turquino (1,974 m (6,476 ft)).
The second-largest island is Isla de la Juventud (Isle of Youth) in the Canarreos archipelago, with an area of 2,200 km2 (849 sq mi). Cuba has an official area (land area) of 109,884 km2 (42,426 sq mi). Its area is 110,860 km2 (42,803 sq mi) including coastal and territorial waters.
Climate
Main article: Climate of Cuba
Viñales ValleyWith the entire island south of the Tropic of Cancer, the local climate is tropical, moderated by northeasterly trade winds that blow year-round. The temperature is also shaped by the Caribbean current, which brings in warm water from the equator. This makes the climate of Cuba warmer than that of Hong Kong, which is at around the same latitude as Cuba but has a subtropical rather than a tropical climate. In general (with local variations), there is a drier season from November to April, and a rainier season from May to October. The average temperature is 21 °C (69.8 °F) in January and 27 °C (80.6 °F) in July. The warm temperatures of the Caribbean Sea and the fact that Cuba sits across the entrance to the Gulf of Mexico combine to make the country prone to frequent hurricanes. These are most common in September and October.
José Martí International Airport Havana
Ignacio Agramonte International Airport Camagüey
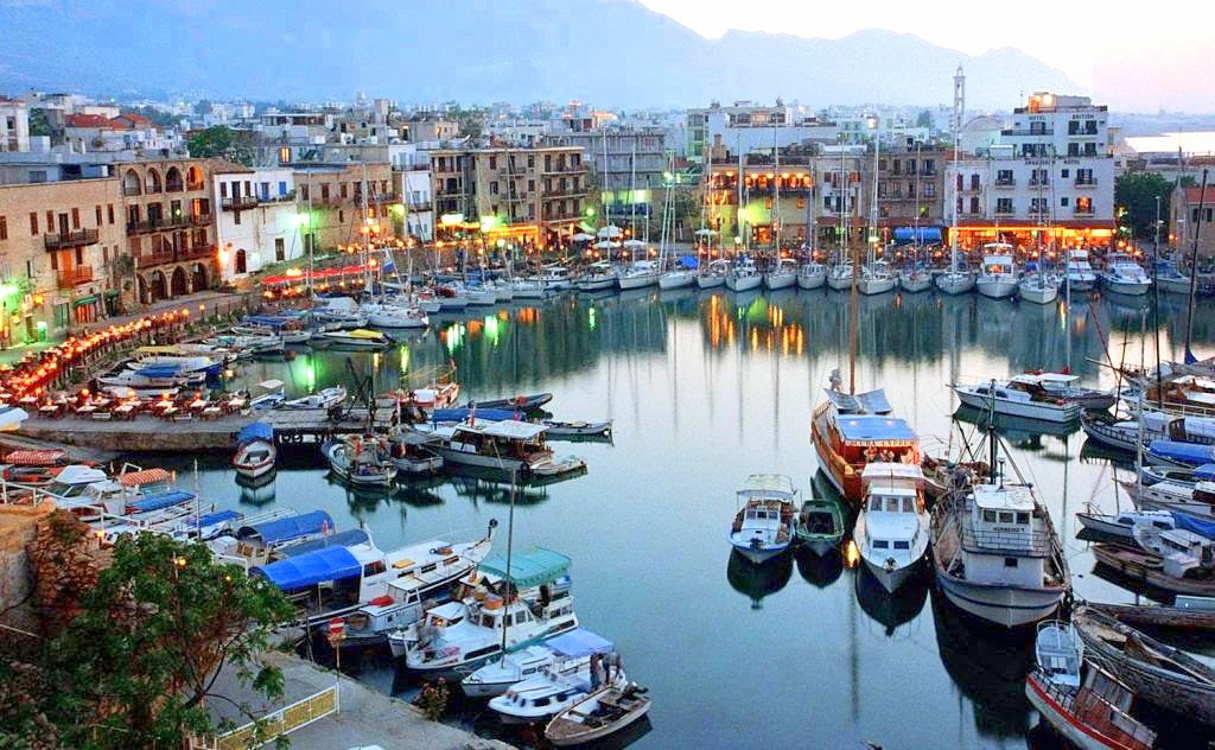
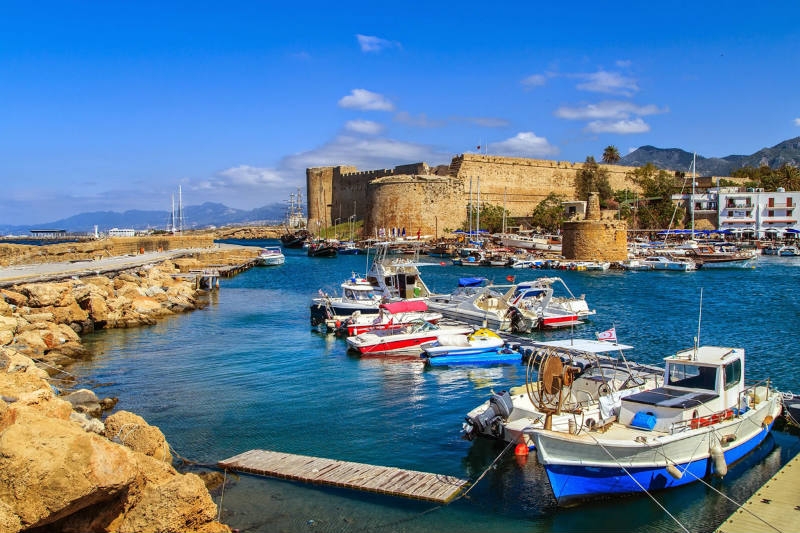
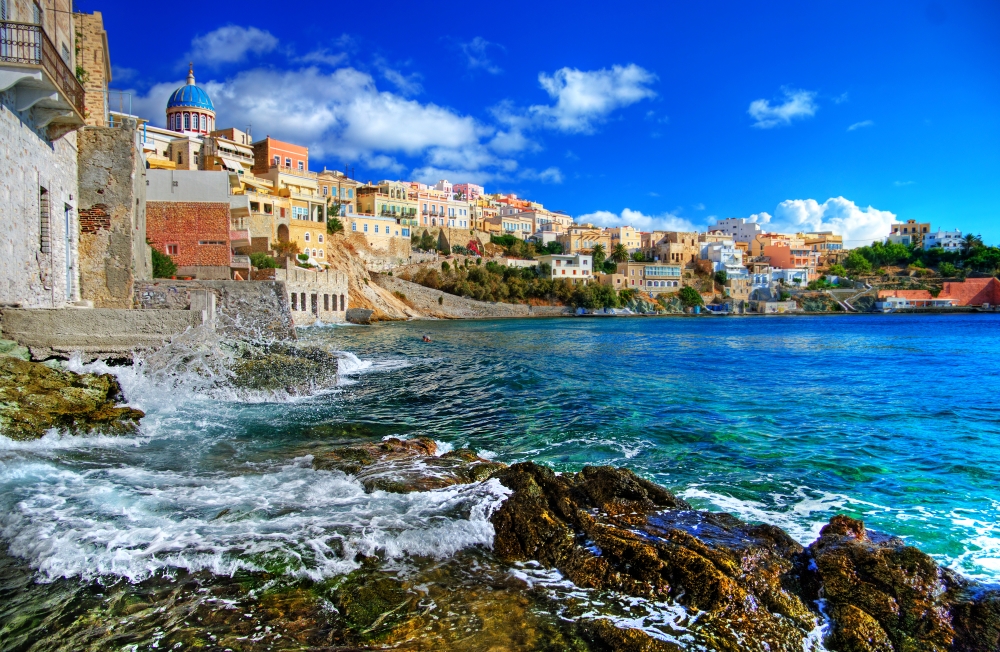
Cyprus
The ancient settlement of Amathus and Choirokoitia; a sanctuary of Aphrodite; painted churches of Troodos; wrecks of the RS Zenobia, the HMS Cricket and the Lady Thetis; and abundant marine life of Akrotiri, Green Bay and Manijin Island
Cyprus, officially named the Republic of Cyprus, is an island state in the eastern part of Mediterranean Sea. Cyprus is located north of Egypt, south of Turkey, east of Greece, northwest of Israel, and west of Syria and Lebanon. Cyprus is the third largest island in the Mediterranean Sea – its total area is about 9.3 thousand square kilometers; and the population is more than 1 million people. The capital of the country is Nicosia. The official languages are Greek and Turkish.
The terrain of the country consists of two mountain ranges and the central plain. The climate is subtropical.
The national currency is the Euro.
Cyprus has long been a favorite vacation spot. The turquoise Mediterranean Sea, palm and olive trees, exotic flowers, comfortable hotels, chic restaurants and many more other things attract tourists from all over the world. Located at the crossroads of East and West, Cyprus has a very unusual character. His story began more than 9000 years. The Assyrians, Egyptians, Persians, Romans Ottomans, and the British took interest in this island in different times and all of them influenced its wonderful and unique culture.
One of the top tourist attractions in Cyprus is the ancient settlement of Amathus, which was founded as an Eteocyprians village about 1050 BC. Connoisseurs of ancient history will be also glad to see Kalavasos-Tenta, a New Stone Age settlement; Choirokoitia, where you can still see several circular huts, created about 9 thousand years ago; Curium, the remains of Roman and Byzantine buildings constructed around 4500-3900 BC; the well-preserved Tombs of the Kings near Paphos and Palaepaphos, a sanctuary of Aphrodite erected in 1200 BC. More recent architectural and historic monuments of this beautiful island include painted churches and monasteries of Troodos, Kyrenia Castle, Kykkos Monastery, Saint Hilarion Castle and lots of other interesting sites.
The nature of Cyprus is not less interesting than its rich culture – here you can enjoy almost pristine landscapes of Akamas Peninsula; bask on the north-coast beaches; watch green and loggerhead turtles and rare moufflons; go biking, horse-riding or hiking in Cyprus mountains or dive in its azure waters.
Larnaca International Airport (LCA) the main international airport of Cyprus located 4 kilometers from Larnaca.
Paphos International Airport (PFO), located near the city of Paphos, serves the western part of Cyprus